|
|
@@ -1,2213 +0,0 @@
|
|
|
-## Django知识点概述
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-### Web应用
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
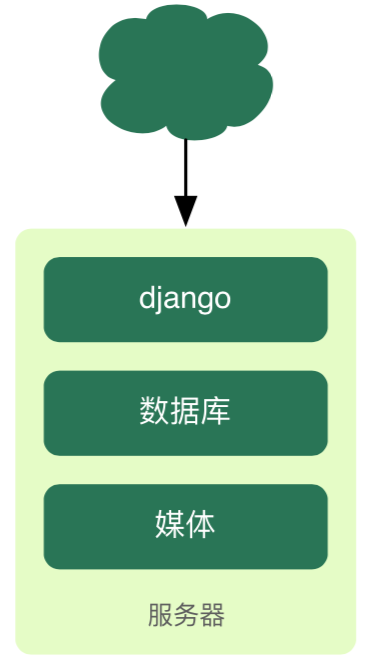
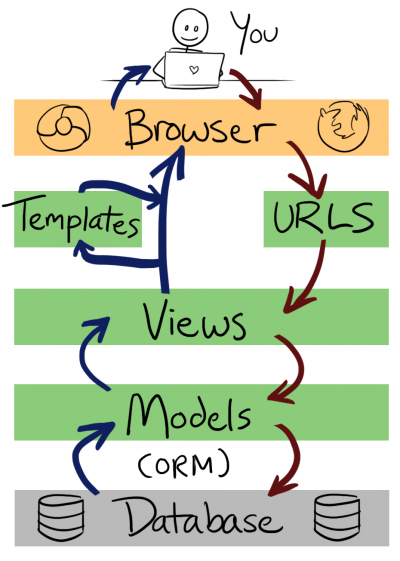
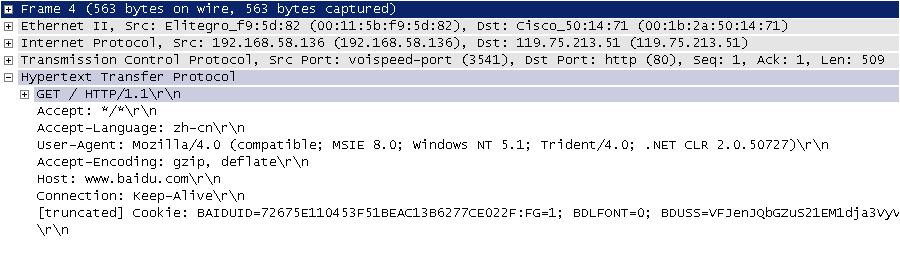
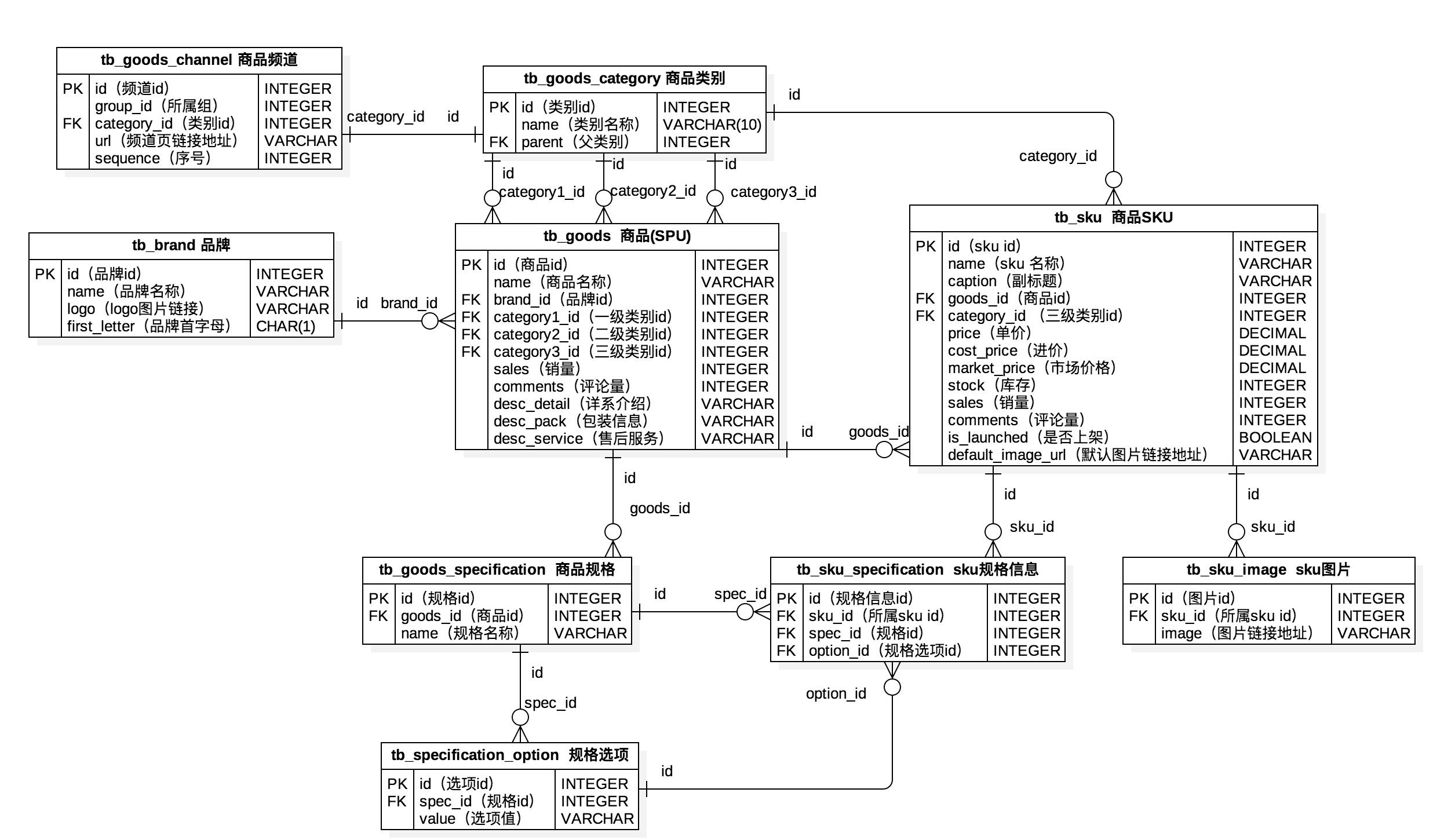
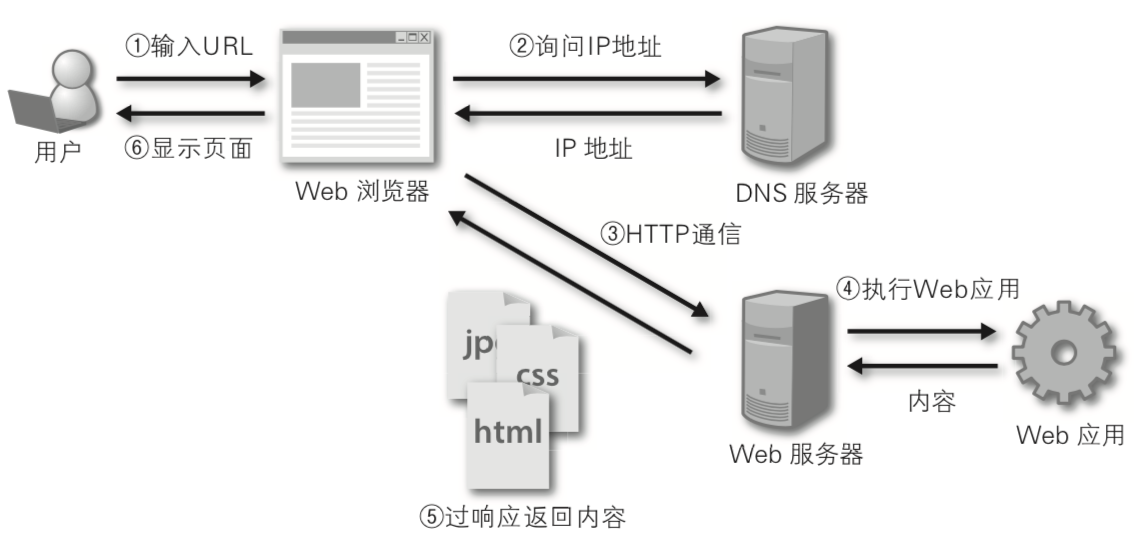
-问题1:描述一个Web应用的工作流程。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
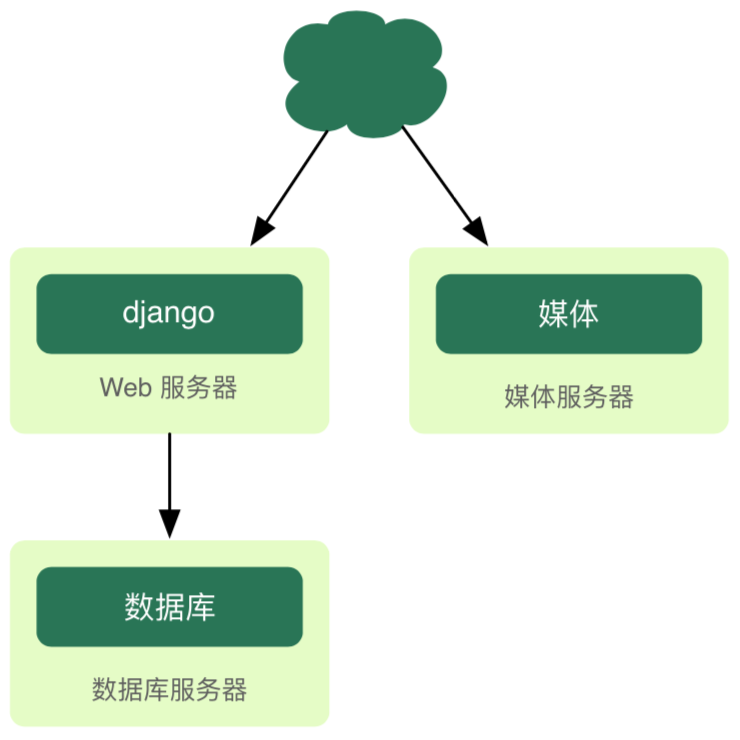
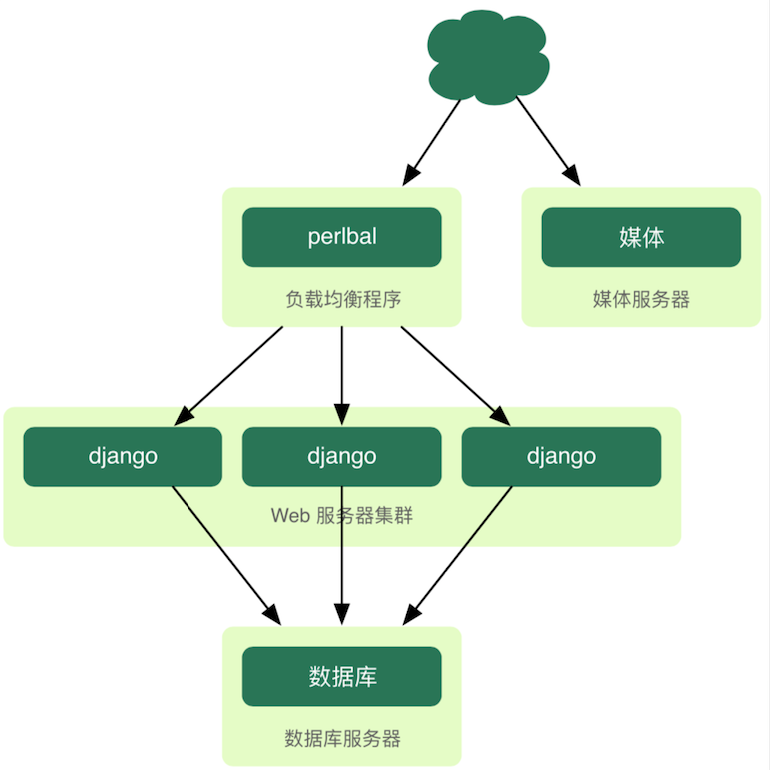
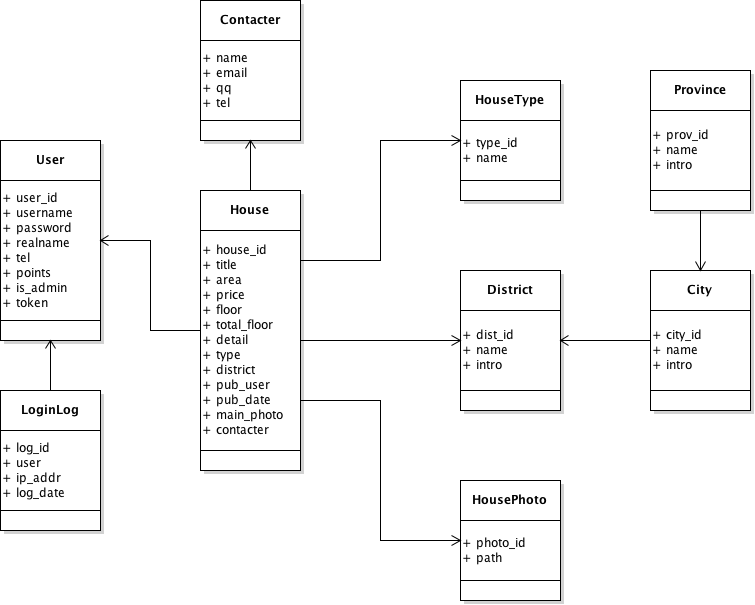
-问题2:描述项目的物理架构。(上图中补充负载均衡(反向代理)服务器、数据库服务器、文件服务器、邮件服务器、缓存服务器、防火墙等,而且每个节点都有可能是多节点构成的集群,如下图所示)
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
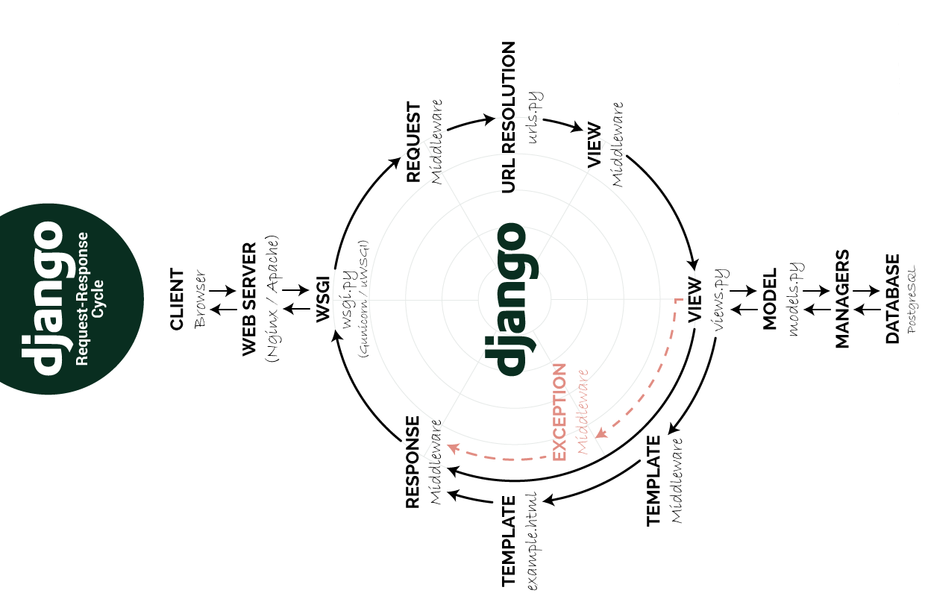
-问题3:描述Django项目的工作流程。(如下图所示)
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-### MVC架构模式
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
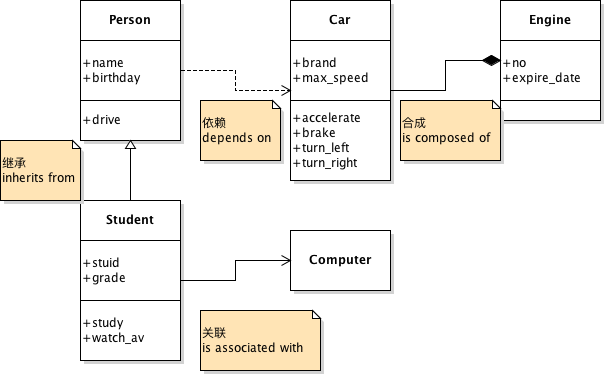
-问题1:为什么要使用MVC架构模式?(模型和视图解耦合)
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
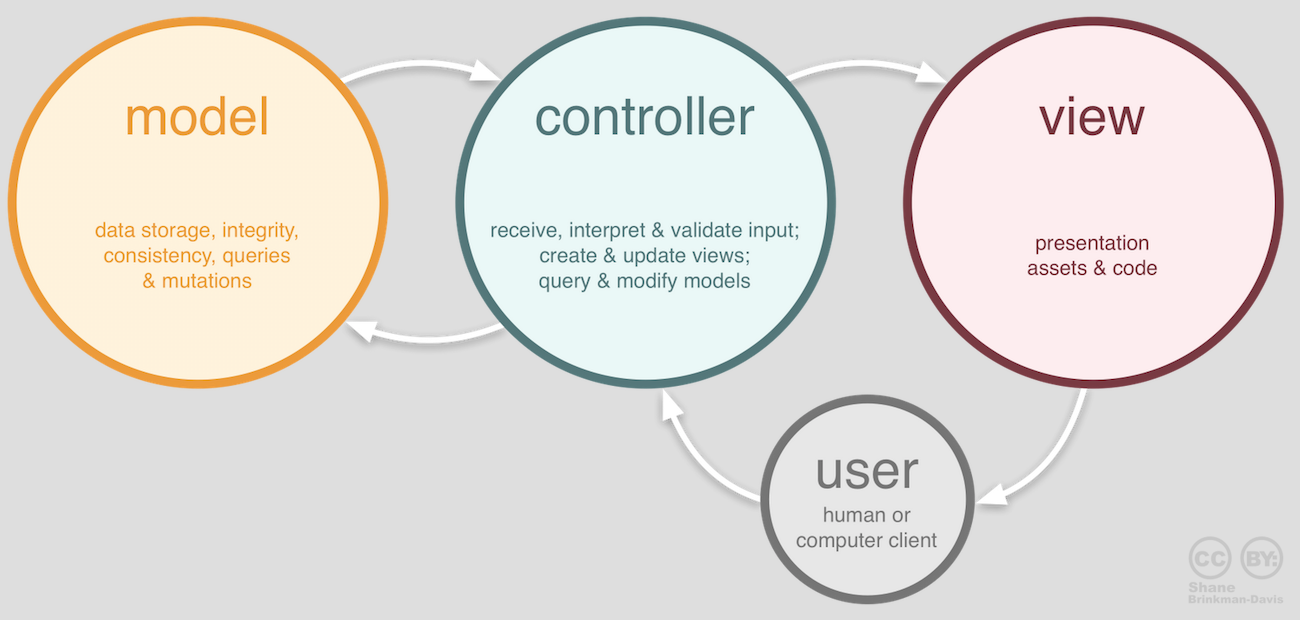
-问题2:MVC架构中每个部分的作用?(如下图所示)
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-### HTTP请求和响应
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-#### HTTP请求 = 请求行+请求头+空行+[消息体]
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-#### HTTP响应 = 响应行+响应头+空行+消息体
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-1. `HTTPRequest`对象的属性和方法:
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - `method` - 获取请求方法
|
|
|
- - `path` / `get_full_path()` - 获取请求路径/带查询字符串的路径
|
|
|
- - `scheme` / `is_secure()` / `get_host()` / `get_port()` - 获取请求的协议/主机/端口
|
|
|
- - `META` / `COOKIES` - 获取请求头/Cookie信息
|
|
|
- - `GET` / `POST` / `FILES` - 获取GET或POST请求参数/上传的文件
|
|
|
- - `get_signed_cookie()` - 获取带签名的Cookie
|
|
|
- - `is_ajax()` - 是不是Ajax异步请求
|
|
|
- - `body` / `content_type` / `encoding` - 获取请求的消息体(bytes流)/MIME类型/编码
|
|
|
-2. 中间件添加的属性:
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - `session` / `user` / `site`
|
|
|
-3. `HttpResponse`对象的属性和方法:
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - `set_cookie()` / `set_signed_cookie()` / `delete_cookie()` - 添加/删除Cookie
|
|
|
- - `__setitem__` / `__getitem__` / `__delitem__` - 添加/获取/删除响应头
|
|
|
- - `charset` / `content` / `status_code` - 响应的字符集/消息体(bytes流)/状态码
|
|
|
- - 1xx:请求已经收到,继续处理
|
|
|
- - 2xx(成功):请求已经成功收到、理解和接收。
|
|
|
- - 3xx(重定向):为完成请求要继续执行后续的操作。
|
|
|
- - 4xx(客户端错误):请求不正确或不能够被受理。
|
|
|
- - 5xx(服务器错误):服务器处理请求失败。
|
|
|
-4. `JsonResponse`(`HttpResponse`的子类型)对象
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Python
|
|
|
- >>> from django.http import HttpResponse, JsonResponse
|
|
|
- >>>
|
|
|
- >>> response = JsonResponse({'foo': 'bar'})
|
|
|
- >>> response.content
|
|
|
- >>>
|
|
|
- >>> response = JsonResponse([1, 2, 3], safe=False)
|
|
|
- >>> response.content
|
|
|
- >>>
|
|
|
- >>> response = HttpResponse(b'...')
|
|
|
- >>> response['cotent-type'] = 'application/pdf';
|
|
|
- >>> response['content-disposition'] = 'inline; filename="xyz.pdf"'
|
|
|
- >>> response['content-disposition'] = 'attachment; filename="xyz.pdf"'
|
|
|
- >>>
|
|
|
- >>> response.set_signed_cookie('foo', 'bar', salt='')
|
|
|
- >>> response.status_code = 200
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-### 数据模型(Model)
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-问题1:关系型数据库表的设计应该注意哪些问题(范式理论和逆范式)?如何通过表来创建模型类(反向工程)?如何通过模型类来创建表(正向工程)?
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-```Shell
|
|
|
-python manage.py makemigrations <appname>
|
|
|
-python manage.py migrate
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-python manage.py inspectdb > <appname>/models.py
|
|
|
-```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-问题2:关系型数据库中数据完整性指的是什么?什么时候需要牺牲数据完整性?(实体完整性/参照完整性/域完整性)
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-问题3:ORM是什么以及解决了什么问题?(对象模型-关系模型双向转换)
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-1. `Field`及其子类的属性:
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - 通用选项:
|
|
|
- - `db_column` / `db_tablespace`
|
|
|
- - `null` / `blank` / `default`
|
|
|
- - `primary_key`
|
|
|
- - `db_index` / `unqiue`
|
|
|
- - `choices` / `help_text` / `error_message` / `editable` / `hidden`
|
|
|
- - 其他选项:
|
|
|
- - `CharField`: `max_length`
|
|
|
- - `DateField`: `auto_now` / `auto_now_add`
|
|
|
- - `DecimalField`: `max_digits` / `decimal_places`
|
|
|
- - `FileField`: `storage` / `upload_to`
|
|
|
- - `ImageField`: `height_field` / `width_field`
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-2. `ForeignKey`的属性:
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - 重要属性:
|
|
|
- - `db_constraint`(提升性能或者数据分片的情况可能需要设置为False)
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - `on_delete`
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- * `CASCADE`:级联删除。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - `PROTECT`:抛出`ProtectedError`异常,阻止删除引用的对象。
|
|
|
- - `SET_NULL`:把外键设置为`null`,当`null`属性被设置为`True`时才能这么做。
|
|
|
- - `SET_DEFAULT`:把外键设置为默认值,提供了默认值才能这么做。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - `related_name`
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Python
|
|
|
- class Dept(models.Model):
|
|
|
- pass
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- class Emp(models.Model):
|
|
|
- dept = models.ForeignKey(related_name='+', ...)
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- Dept.objects.get(no=10).emp_set.all()
|
|
|
- Emp.objects.filter(dept__no=10)
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- > 说明:`related_name`设置为`'+'`,可以防止一对多外键关联从“一”的一方查询“多”的一方。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - 其他属性:
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - `to_field` / `limit_choices_to` / `swappable`
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-3. `Model`的属性和方法
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - `objects` / `pk`
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - `save()` / `delete()`
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - `clean()` / `validate_unique()` / `full_clean()`
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-4. `QuerySet`的方法
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - `get()` / `all()` / `values()`
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- > 说明:`values()`返回的`QuerySet`中不是模型对象而是字典
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - `count()` / `order_by()` / `exists()` / `reverse()`
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - `filter()` / `exclude()`
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - `exact` / `iexact`:精确匹配/忽略大小写的精确匹配查询
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - `contains` / `icontains` / `startswith / istartswith / endswith / iendswith`:基于`like`的模糊查询
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - `in`:集合运算
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - `gt` / `gte` / `lt` / `lte`:大于/大于等于/小于/小于等于关系运算
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - `range`:指定范围查询(SQL中的`between…and…`)
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - `year` / `month` / `day` / `week_day` / `hour` / `minute` / `second`:查询时间日期
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - `isnull`:查询空值(`True`)或非空值(`False`)
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - `search`:基于全文索引的全文检索
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - `regex` / `iregex`:基于正则表达式的模糊匹配查询
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - `aggregate()` / `annotate()`
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - `Avg` / `Count` / `Sum` / `Max` / `Min`
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Python
|
|
|
- >>> from django.db.models import Avg
|
|
|
- >>> Emp.objects.aggregate(avg_sal=Avg('sal'))
|
|
|
- (0.001) SELECT AVG(`TbEmp`.`sal`) AS `avg_sal` FROM `TbEmp`; args=()
|
|
|
- {'avg_sal': 3521.4286}
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Python
|
|
|
- >>> Emp.objects.values('dept').annotate(total=Count('dept'))
|
|
|
- (0.001) SELECT `TbEmp`.`dno`, COUNT(`TbEmp`.`dno`) AS `total` FROM `TbEmp` GROUP BY `TbEmp`.`dno` ORDER BY NULL LIMIT 21; args=()
|
|
|
- <QuerySet [{'dept': 10, 'total': 4}, {'dept': 20, 'total': 7}, {'dept': 30, 'total': 3}]
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - `first()` / `last()`
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- > 说明:调用`first()`方法相当于用`[0]`对`QuerySet`进行切片。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - `only()` / `defer()`
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Python
|
|
|
- >>> Emp.objects.filter(pk=7800).only('name', 'sal')
|
|
|
- (0.001) SELECT `TbEmp`.`empno`, `TbEmp`.`ename`, `TbEmp`.`sal` FROM `TbEmp` WHERE `TbEmp`.`empno` = 7800 LIMIT 21; args=(7800,)
|
|
|
- <QuerySet [<Emp: Emp object (7800)>]>
|
|
|
- >>> Emp.objects.filter(pk=7800).defer('name', 'sal')
|
|
|
- (0.001) SELECT `TbEmp`.`empno`, `TbEmp`.`job`, `TbEmp`.`mgr`, `TbEmp`.`comm`, `TbEmp`.`dno` FROM `TbEmp` WHERE `TbEmp`.`empno` = 7800 LIMIT 21; args=(7800,)
|
|
|
- <QuerySet [<Emp: Emp object (7800)>]>
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - `create()` / `update()` / `raw()`
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Python
|
|
|
- >>> Emp.objects.filter(dept__no=20).update(sal=F('sal') + 100)
|
|
|
- (0.011) UPDATE `TbEmp` SET `sal` = (`TbEmp`.`sal` + 100) WHERE `TbEmp`.`dno` = 20; args=(100, 20)
|
|
|
- >>>
|
|
|
- >>> Emp.objects.raw('select empno, ename, job from TbEmp where dno=10')
|
|
|
- <RawQuerySet: select empno, ename, job from TbEmp where dno=10>
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-5. `Q`对象和`F`对象
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Python
|
|
|
- >>> from django.db.models import Q
|
|
|
- >>> Emp.objects.filter(
|
|
|
- ... Q(name__startswith='张'),
|
|
|
- ... Q(sal__lte=5000) | Q(comm__gte=1000)
|
|
|
- ... ) # 查询名字以“张”开头且工资小于等于5000或补贴大于等于1000的员工
|
|
|
- <QuerySet [<Emp: 张三丰>]>
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Python
|
|
|
- reporter = Reporters.objects.filter(name='Tintin')
|
|
|
- reporter.update(stories_filed=F('stories_filed') + 1)
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-6. 原生SQL查询
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Python
|
|
|
- from django.db import connection
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- with connection.cursor() as cursor:
|
|
|
- cursor.execute("UPDATE TbEmp SET sal=sal+10 WHERE dno=30")
|
|
|
- cursor.execute("SELECT ename, job FROM TbEmp WHERE dno=10")
|
|
|
- row = cursor.fetchall()
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-7. 模型管理器
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Python
|
|
|
- class BookManager(models.Manager):
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- def title_count(self, keyword):
|
|
|
- return self.filter(title__icontains=keyword).count()
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-### 视图函数(Controller)
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-#### 如何设计视图函数
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-1. 用户的每个操作对应一个视图函数。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-2. [每个视图函数可以构成一个事务边界](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/2.1/ref/settings/)。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - 事务的ACID特性。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - 原子性(Atomicity):事务中各项的操作要么全做要么全不做;
|
|
|
- - 一致性(Consistentcy):事务前后系统的状态是一致的;
|
|
|
- - 隔离性(Isolation):并发执行的事务无法看到彼此的中间状态;
|
|
|
- - 持久性(Duration):事务完成后所做的改动都会被持久化。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - 事务隔离级别 - 设置事务隔离级别是为了数据库底层依据事务隔离级别为数据加上适当的锁。如果需要保证数据的强一致性,那么关系型数据库仍然是唯一的也是最好的选择,因为关系型数据库可以通过锁机制来保护数据。事务隔离级别从低到高依次是:Read Uncommitted(读未提交)、Read Committed(读提交)、Repeatable Read(可重复读)、Serializable(串行化)。事务隔离级别越高,数据并发访问的问题越少,但是性能越差;事务隔离级别越低,数据并发访问的问题越多,但是性能越好。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - 数据并发访问会产生5种问题(请参考我的[《Java面试题全集(上)》](https://blog.csdn.net/jackfrued/article/details/44921941)第80题对该问题的讲解):
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - 第1类丢失更新(A事务撤销覆盖B事务更新的数据)和第2类丢失更新(A事务提交覆盖B事务更新的数据)。
|
|
|
- - 脏读(读脏数据):一个事务读取到其他尚未提交的事务的数据。
|
|
|
- - 不可重复读: 一个事务在读取它的查询结果时,被另一个事务更新了它的查询记录导致无法读到数据。
|
|
|
- - 幻读:一个事务在读取它的查询结果时,发现读到了被另一个事务提交的新数据。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```SQL
|
|
|
- -- 设置全局默认的事务隔离级别
|
|
|
- set global transaction isolation level repeatable read;
|
|
|
- -- 设置当前会话的事务隔离级别
|
|
|
- set session transaction isolation level read committed;
|
|
|
- -- 查询当前会话的事务隔离级别
|
|
|
- select @@tx_isolation;
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - Django中的事务控制。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - 给每个请求绑定事务环境(反模式)。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Python
|
|
|
- ATOMIC_REQUESTS = True
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - 使用事务装饰器(简单易用)。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Python
|
|
|
- @transaction.non_atomic_requests
|
|
|
- @transaction.atomic
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - 使用上下文语法(事务控制的范围更加精准)。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Python
|
|
|
- with transaction.atomic():
|
|
|
- pass
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - 关闭自动提交使用手动提交。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Python
|
|
|
- AUTOCOMMIT = False
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Python
|
|
|
- transaction.commit()
|
|
|
- transaction.rollback()
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-#### URL配置
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-1. 可以让部分URL只在调试模式下生效。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Python
|
|
|
- from django.conf import settings
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- urlpatterns = [
|
|
|
- ...
|
|
|
- ]
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- if settings.DEBUG:
|
|
|
- urlpatterns += [ ... ]
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-2. 可以使用命名捕获组捕获路径参数。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Python
|
|
|
- url(r'api/code/(?P<mobile>1[3-9]\d{9})'),
|
|
|
- path('api/code/<str:mobile>'),
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-3. URL配置不关心请求使用的方法(一个视图函数可以处理不同的请求方式)。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-4. 如果使用`url`函数捕获的路径参数都是字符串,`path`函数可以指定路径参数类型。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-5. 可以使用`include`函数引入其他URL配置,捕获的参数会向下传递。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-6. 在`url`和`path`函数甚至是`include`函数中都可以用字典向视图传入额外的参数,如果参数与捕获的参数同名,则使用字典中的参数。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-7. 可以用`reverse`函数实现URL的逆向解析(从名字解析出URL),在模板中也可以用`{% url %}`实现同样的操作。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Python
|
|
|
- path('', views.index, name='index')
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- return redirect(reverse('index'))
|
|
|
- return redirect('index')
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-### 模板(View)
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-#### 后端渲染
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-1. 模板的配置和渲染函数。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Python
|
|
|
- TEMPLATES = [
|
|
|
- {
|
|
|
- 'BACKEND': 'django.template.backends.django.DjangoTemplates',
|
|
|
- 'DIRS': [os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'templates'), ],
|
|
|
- 'APP_DIRS': True,
|
|
|
- 'OPTIONS': {
|
|
|
- 'context_processors': [
|
|
|
- 'django.template.context_processors.debug',
|
|
|
- 'django.template.context_processors.request',
|
|
|
- 'django.contrib.auth.context_processors.auth',
|
|
|
- 'django.contrib.messages.context_processors.messages',
|
|
|
- ],
|
|
|
- },
|
|
|
- },
|
|
|
- ]
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Python
|
|
|
- resp = render(request, 'index.html', {'foo': ...})
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-2. 模板遇到变量名的查找顺序。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - 字典查找(如:`foo['bar']`)
|
|
|
- - 属性查找(如:`foo.bar`)
|
|
|
- - 方法调用(如:`foo.bar()`)
|
|
|
- - 方法不能有必须传值的参数
|
|
|
- - 在模板中不能够给方法传参
|
|
|
- - 如果方法的`alters_data`被设置为`True`则不能调用该方法(避免误操作的风险),模型对象动态生成的`delete()`和`save()`方法都设定了`alters_data = True`。
|
|
|
- - 列表索引查找(如:`foo[0]`)
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-3. 模板标签的使用。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - `{% if %}` / `{% else %}` / `{% endif %}`
|
|
|
- - `{% for %}` / `{% endfor %}`
|
|
|
- - `{% ifequal %}` / `{% endifequal %}` / `{% ifnotequal %}` / `{% endifnotequal %}`
|
|
|
- - `{# comment #}` / `{% comment %}` / `{% endcomment %}`
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-4. 过滤器的使用。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - `lower` / `upper` / `first` / `last` / `truncatewords` / `date `/ `time` / `length` / `pluralize` / `center` / `ljust` / `rjust` / `cut` / `urlencode` / `default_if_none` / `filesizeformat` / `join` / `slice` / `slugify`
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-5. 模板的包含和继承。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - `{% include %}` / `{% block %}`
|
|
|
- - `{% extends %}`
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-6. 模板加载器(后面优化部分会讲到)。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - 文件系统加载器
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Python
|
|
|
- TEMPLATES = [{
|
|
|
- 'BACKEND': 'django.template.backends.django.DjangoTemplates',
|
|
|
- 'DIRS': [os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'templates')],
|
|
|
- }]
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - 应用目录加载器
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Python
|
|
|
- TEMPLATES = [{
|
|
|
- 'BACKEND': 'django.template.backends.django.DjangoTemplates',
|
|
|
- 'APP_DIRS': True,
|
|
|
- }]
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-#### 前端渲染
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-1. 前端模板引擎:Handlebars / Mustache。
|
|
|
-2. 前端MV\*框架。
|
|
|
- - MVC - AngularJS
|
|
|
- - MVVM - Vue.js
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-#### 其他视图
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-1. MIME(多用途Internet邮件扩展)类型 - 告知浏览器传输的数据类型。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- | Content-Type | 说明 |
|
|
|
- | ---------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
|
|
- | application/json | [JSON](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/JSON)(JavaScript Object Notation) |
|
|
|
- | application/pdf | [PDF](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/PDF)(Portable Document Format) |
|
|
|
- | audio/mpeg | [MP3](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/MP3)或其他[MPEG](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/MPEG)音频文件 |
|
|
|
- | audio/vnd.wave | [WAV](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/WAV)音频文件 |
|
|
|
- | image/gif | [GIF](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/GIF)图像文件 |
|
|
|
- | image/jpeg | [JPEG](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/JPEG)图像文件 |
|
|
|
- | image/png | [PNG](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/PNG)图像文件 |
|
|
|
- | text/html | [HTML](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/HTML)文件 |
|
|
|
- | text/xml | [XML](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/XML) |
|
|
|
- | video/mp4 | [MP4](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/MP4)视频文件 |
|
|
|
- | video/quicktime | [QuickTime](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/QuickTime)视频文件 |
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-2. 如何处置生成的内容(inline / attachment)。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Python
|
|
|
- >>> from urllib.parse import quote
|
|
|
- >>>
|
|
|
- >>> response['content-type'] = 'application/pdf'
|
|
|
- >>> filename = quote('Python语言规范.pdf')
|
|
|
- >>> filename
|
|
|
- 'Python%E8%AF%AD%E8%A8%80%E8%A7%84%E8%8C%83.pdf'
|
|
|
- >>> response['content-disposition'] = f'attachment; filename="{filename}"'
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
- > 提醒:URL以及请求和响应头中的中文都应该处理成[百分号编码](https://zh.wikipedia.org/zh-hans/%E7%99%BE%E5%88%86%E5%8F%B7%E7%BC%96%E7%A0%81)。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-3. 生成CSV / Excel / PDF / 统计报表。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - 向浏览器传输二进制数据。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Python
|
|
|
- buffer = ByteIO()
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- resp = HttpResponse(content_type='...')
|
|
|
- resp['Content-Disposition'] = 'attachment; filename="..."'
|
|
|
- resp.write(buffer.getvalue())
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - 大文件的流式处理:`StreamingHttpResponse`。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Python
|
|
|
- def download_file(request):
|
|
|
- file_stream = open('...', 'rb')
|
|
|
- # 如果文件的二进制数据较大则最好用迭代器进行处理避免过多的占用服务器内存
|
|
|
- file_iter = iter(lambda: file_stream.read(4096), b'')
|
|
|
- resp = StreamingHttpResponse(file_iter)
|
|
|
- # 中文文件名要处理成百分号编码
|
|
|
- filename = quote('...', 'utf-8')
|
|
|
- resp['Content-Type'] = '...'
|
|
|
- resp['Content-Disposition'] = f'attachment; filename="{filename}"'
|
|
|
- return resp
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- > 说明:如果需要生成PDF文件,可以需要安装`reportlab`;生成Excel可以使用`openpyxl`或`xlrd`。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - [ECharts](http://echarts.baidu.com/)或[Chart.js](https://www.chartjs.org/)。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - 思路:后端只提供JSON格式的数据,前端JavaScript渲染生成图表。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-### 中间件
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-问题1:中间件背后的设计理念是什么?(分离横切关注功能/拦截过滤器模式)
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-问题2:中间件有哪些不同的实现方式?(参考下面的代码)
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-问题3:描述Django内置的中间件及其执行顺序。(推荐阅读:[Django官方文档 - 中间件 - 中间件顺序](https://docs.djangoproject.com/zh-hans/2.0/ref/middleware/#middleware-ordering))
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-#### 激活中间件
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-```Python
|
|
|
-MIDDLEWARE = [
|
|
|
- 'django.middleware.security.SecurityMiddleware',
|
|
|
- 'django.contrib.sessions.middleware.SessionMiddleware',
|
|
|
- 'django.middleware.common.CommonMiddleware',
|
|
|
- 'django.middleware.csrf.CsrfViewMiddleware',
|
|
|
- 'django.contrib.auth.middleware.AuthenticationMiddleware',
|
|
|
- 'django.contrib.messages.middleware.MessageMiddleware',
|
|
|
- 'django.middleware.clickjacking.XFrameOptionsMiddleware',
|
|
|
- 'common.middlewares.block_sms_middleware',
|
|
|
-]
|
|
|
-```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-#### 自定义中间件
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-```Python
|
|
|
-def simple_middleware(get_response):
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- def middleware(request):
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- response = get_response(request)
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- return response
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- return middleware
|
|
|
-```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-```Python
|
|
|
-class MyMiddleware(object):
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- def __init__(self, get_response):
|
|
|
- self.get_response = get_response
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- def __call__(self, request):
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- response = self.get_response(request)
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- return response
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- def process_view(self, request, view_func, view_args, view_kwargs):
|
|
|
- response = view_func(*view_args, **view_kwargs)
|
|
|
- return response
|
|
|
-```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-```Python
|
|
|
-class MyMiddleware(object):
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- def __init__(self):
|
|
|
- pass
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- def process_request(request):
|
|
|
- pass
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- def process_view(request, view_func, view_args, view_kwargs):
|
|
|
- pass
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- def process_template_response(request, response):
|
|
|
- pass
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- def process_response(request, response):
|
|
|
- pass
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- def process_exception(request, exception):
|
|
|
- pass
|
|
|
-```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-#### 内置中间件
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-1. CommonMiddleware - 基础设置中间件
|
|
|
- - DISALLOWED_USER_AGENTS - 不被允许的用户代理(浏览器)
|
|
|
- - APPEND_SLASH - 是否追加`/`
|
|
|
- - USE_ETAG - 浏览器缓存相关
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-2. SecurityMiddleware - 安全相关中间件
|
|
|
- - SECURE_HSTS_SECONDS - 强制使用HTTPS的时间
|
|
|
- - SECURE_HSTS_INCLUDE_SUBDOMAINS - HTTPS是否覆盖子域名
|
|
|
- - SECURE_CONTENT_TYPE_NOSNIFF - 是否允许浏览器推断内容类型
|
|
|
- - SECURE_BROWSER_XSS_FILTER - 是否启用跨站脚本攻击过滤器
|
|
|
- - SECURE_SSL_REDIRECT - 是否重定向到HTTPS连接
|
|
|
- - SECURE_REDIRECT_EXEMPT - 免除重定向到HTTPS
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-3. SessionMiddleware - 会话中间件
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-4. CsrfViewMiddleware - 防范跨站身份伪造中间件
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-5. XFrameOptionsMiddleware - 防范点击劫持攻击中间件
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- 
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-### 表单
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-1. 用法:通常不要用来生成页面上的表单控件(耦合度太高不容易定制),主要用来验证数据。
|
|
|
-2. Form的属性和方法:
|
|
|
- - `is_valid()` / `is_multipart()`
|
|
|
- - `errors` / `fields` / `is_bound` / `changed_data` / `cleaned_data`
|
|
|
- - `add_error()` / `has_errors()` / `non_field_errors()`
|
|
|
- - `clean()`
|
|
|
-3. Form.errors的方法:
|
|
|
- - `as_data()` / `as_json()` / `get_json_data()`
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-问题1:Django中的`Form`和`ModelForm`有什么作用?(通常不用来生成表单主要用来验证数据)
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-问题2:表单上传文件时应该注意哪些问题?(表单的设置、多文件上传、图片预览、Ajax上传文件、上传后的文件如何存储)
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-### Cookie和Session
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-问题1:使用Cookie能解决什么问题?(用户跟踪,解决HTTP协议无状态问题)
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-1. URL重写
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
- http://www.abc.com/path/resource?foo=bar
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-2. 隐藏域(隐式表单域)
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```HTML
|
|
|
- <form action="" method="post">
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- <input type="hidden" name="foo" value="bar">
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- </form>
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-3. Cookie
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-问题2:Cookie和Session之间关系是什么?(Session的标识通过Cookie保存和传输)
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-#### Session的配置
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-1. Session对应的中间件:`django.contrib.sessions.middleware.SessionMiddleware`。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-2. Session引擎。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - 基于数据库(默认方式)
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Python
|
|
|
- INSTALLED_APPS = [
|
|
|
- 'django.contrib.sessions',
|
|
|
- ]
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - 基于缓存(推荐使用)
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Python
|
|
|
- SESSION_ENGINE = 'django.contrib.sessions.backends.cache'
|
|
|
- SESSION_CACHE_ALIAS = 'session'
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - 基于文件(基本不考虑)
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - 基于Cookie(不靠谱)
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Python
|
|
|
- SESSION_ENGINE = 'django.contrib.sessions.backends.signed_cookies'
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-3. Cookie相关的配置。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Python
|
|
|
- SESSION_COOKIE_NAME = 'djang_session_id'
|
|
|
- SESSION_COOKIE_AGE = 1209600
|
|
|
- SESSION_EXPIRE_AT_BROWSER_CLOSE = False
|
|
|
- SESSION_SAVE_EVERY_REQUEST = False
|
|
|
- SESSION_COOKIE_HTTPONLY = True
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-4. session的属性和方法。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - `session_key` / `session_data` / `expire_date`
|
|
|
- - `__getitem__` / `__setitem__` / `__delitem__` / `__contains__`
|
|
|
- - `set_expiry()` / `get_expiry_age()` / `get_expiry_date()` - 设置/获取会话超期时间
|
|
|
- - `flush()` - 销毁会话
|
|
|
- - `set_test_cookie()` / `test_cookie_worked()` / `delete_test_cookie()` - 测试浏览器是否支持Cookie(提示用户如果浏览器禁用Cookie可能会影响网站的使用)
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-5. session的序列化。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Python
|
|
|
- SESSION_SERIALIZER = 'django.contrib.sessions.serializers.JSONSerializer'
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - JSONSerializer(1.6及以后默认)- 如果想将自定义的对象放到session中,会遇到“Object of type 'XXX' is not JSON serializable”的问题。
|
|
|
- - PickleSerializer(1.6以前的默认)- 因为安全问题不推荐使用,但是只要不去反序列化用户构造的恶意的Payload其实也没有什么风险。关于这种方式的安全漏洞,可以参考《[Python Pickle的任意代码执行漏洞实践和Payload构造》](http://www.polaris-lab.com/index.php/archives/178/)一文或《软件架构-Python语言实现》上关于这个问题的讲解。
|
|
|
- - 说明:如果使用了django_redis整合Redis作为session的存储引擎,那么由于django_redis又封装了一个PickleSerializer来提供序列化,所以不会存在上述的问题,且Redis中保存的value是pickle序列化之后的结果。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-### 缓存
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-#### 配置缓存
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-```Python
|
|
|
-CACHES = {
|
|
|
- # 默认缓存
|
|
|
- 'default': {
|
|
|
- 'BACKEND': 'django_redis.cache.RedisCache',
|
|
|
- 'LOCATION': [
|
|
|
- 'redis://1.2.3.4:6379/0',
|
|
|
- ],
|
|
|
- 'KEY_PREFIX': 'fang',
|
|
|
- 'OPTIONS': {
|
|
|
- 'CLIENT_CLASS': 'django_redis.client.DefaultClient',
|
|
|
- 'CONNECTION_POOL_KWARGS': {
|
|
|
- 'max_connections': 1000,
|
|
|
- },
|
|
|
- 'PASSWORD': '1qaz2wsx',
|
|
|
- }
|
|
|
- },
|
|
|
- # 页面缓存
|
|
|
- 'page': {
|
|
|
- 'BACKEND': 'django_redis.cache.RedisCache',
|
|
|
- 'LOCATION': [
|
|
|
- 'redis://1.2.3.4:6379/1',
|
|
|
- ],
|
|
|
- 'KEY_PREFIX': 'fang:page',
|
|
|
- 'OPTIONS': {
|
|
|
- 'CLIENT_CLASS': 'django_redis.client.DefaultClient',
|
|
|
- 'CONNECTION_POOL_KWARGS': {
|
|
|
- 'max_connections': 500,
|
|
|
- },
|
|
|
- 'PASSWORD': '1qaz2wsx',
|
|
|
- }
|
|
|
- },
|
|
|
- # 会话缓存
|
|
|
- 'session': {
|
|
|
- 'BACKEND': 'django_redis.cache.RedisCache',
|
|
|
- 'LOCATION': [
|
|
|
- 'redis://1.2.3.4:6379/2',
|
|
|
- ],
|
|
|
- 'KEY_PREFIX': 'fang:session',
|
|
|
- 'TIMEOUT': 1209600,
|
|
|
- 'OPTIONS': {
|
|
|
- 'CLIENT_CLASS': 'django_redis.client.DefaultClient',
|
|
|
- 'CONNECTION_POOL_KWARGS': {
|
|
|
- 'max_connections': 2000,
|
|
|
- },
|
|
|
- 'PASSWORD': '1qaz2wsx',
|
|
|
- }
|
|
|
- },
|
|
|
- # 验证码缓存
|
|
|
- 'code': {
|
|
|
- 'BACKEND': 'django_redis.cache.RedisCache',
|
|
|
- 'LOCATION': [
|
|
|
- 'redis://1.2.3.4:6379/3',
|
|
|
- ],
|
|
|
- 'KEY_PREFIX': 'fang:code:tel',
|
|
|
- 'OPTIONS': {
|
|
|
- 'CLIENT_CLASS': 'django_redis.client.DefaultClient',
|
|
|
- 'CONNECTION_POOL_KWARGS': {
|
|
|
- 'max_connections': 500,
|
|
|
- },
|
|
|
- 'PASSWORD': '1qaz2wsx',
|
|
|
- }
|
|
|
- },
|
|
|
-}
|
|
|
-```
|
|
|
-#### 全站缓存
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-```Python
|
|
|
-MIDDLEWARE_CLASSES = [
|
|
|
- 'django.middleware.cache.UpdateCacheMiddleware',
|
|
|
- ...
|
|
|
- 'django.middleware.common.CommonMiddleware',
|
|
|
- ...
|
|
|
- 'django.middleware.cache.FetchFromCacheMiddleware',
|
|
|
-]
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-CACHE_MIDDLEWARE_ALIAS = 'default'
|
|
|
-CACHE_MIDDLEWARE_SECONDS = 300
|
|
|
-CACHE_MIDDLEWARE_KEY_PREFIX = 'djang:cache'
|
|
|
-```
|
|
|
-#### 视图层缓存
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-```Python
|
|
|
-from django.views.decorators.cache import cache_page
|
|
|
-from django.views.decorators.vary import vary_on_cookie
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-@cache_page(timeout=60 * 15, cache='page')
|
|
|
-@vary_on_cookie
|
|
|
-def my_view(request):
|
|
|
- pass
|
|
|
-```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-```Python
|
|
|
-from django.views.decorators.cache import cache_page
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-urlpatterns = [
|
|
|
- url(r'^foo/([0-9]{1,2})/$', cache_page(60 * 15)(my_view)),
|
|
|
-]
|
|
|
-```
|
|
|
-#### 其他内容
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-1. 模板片段缓存。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - `{% load cache %}`
|
|
|
- - `{% cache %}` / `{% endcache %}`
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-2. 使用底层API访问缓存。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Python
|
|
|
- >>> from django.core.cache import cache
|
|
|
- >>>
|
|
|
- >>> cache.set('my_key', 'hello, world!', 30)
|
|
|
- >>> cache.get('my_key')
|
|
|
- >>> cache.clear()
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Python
|
|
|
- >>> from django.core.cache import caches
|
|
|
- >>> cache1 = caches['page']
|
|
|
- >>> cache2 = caches['page']
|
|
|
- >>> cache1 is cache2
|
|
|
- True
|
|
|
- >>> cache3 = caches['session']
|
|
|
- >>> cache2 is cache3
|
|
|
- False
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Python
|
|
|
- >>> from django_redis import get_redis_connection
|
|
|
- >>>
|
|
|
- >>> redis_client = get_redis_connection()
|
|
|
- >>> redis_client.hgetall()
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-### 日志
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-#### 日志级别
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-NOTSET < DEBUG < INFO < WARNING < ERROR < FATAL
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-#### 日志配置
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-```Python
|
|
|
-LOGGING = {
|
|
|
- 'version': 1,
|
|
|
- 'disable_existing_loggers': False,
|
|
|
- # 配置日志格式化器
|
|
|
- 'formatters': {
|
|
|
- 'simple': {
|
|
|
- 'format': '%(asctime)s %(module)s.%(funcName)s: %(message)s',
|
|
|
- 'datefmt': '%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S',
|
|
|
- },
|
|
|
- 'verbose': {
|
|
|
- 'format': '%(asctime)s %(levelname)s [%(process)d-%(threadName)s] '
|
|
|
- '%(module)s.%(funcName)s line %(lineno)d: %(message)s',
|
|
|
- 'datefmt': '%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S',
|
|
|
- }
|
|
|
- },
|
|
|
- # 配置日志过滤器
|
|
|
- 'filters': {
|
|
|
- 'require_debug_true': {
|
|
|
- '()': 'django.utils.log.RequireDebugTrue',
|
|
|
- },
|
|
|
- },
|
|
|
- # 配置日志处理器
|
|
|
- 'handlers': {
|
|
|
- 'console': {
|
|
|
- 'class': 'logging.StreamHandler',
|
|
|
- 'level': 'DEBUG',
|
|
|
- 'filters': ['require_debug_true'],
|
|
|
- 'formatter': 'simple',
|
|
|
- },
|
|
|
- 'file1': {
|
|
|
- 'class': 'logging.handlers.TimedRotatingFileHandler',
|
|
|
- 'filename': 'fang.log',
|
|
|
- 'when': 'W0',
|
|
|
- 'backupCount': 12,
|
|
|
- 'formatter': 'simple',
|
|
|
- 'level': 'INFO',
|
|
|
- },
|
|
|
- 'file2': {
|
|
|
- 'class': 'logging.handlers.TimedRotatingFileHandler',
|
|
|
- 'filename': 'error.log',
|
|
|
- 'when': 'D',
|
|
|
- 'backupCount': 31,
|
|
|
- 'formatter': 'verbose',
|
|
|
- 'level': 'WARNING',
|
|
|
- },
|
|
|
- },
|
|
|
- # 配置日志器
|
|
|
- 'loggers': {
|
|
|
- 'django': {
|
|
|
- 'handlers': ['console', 'file1', 'file2'],
|
|
|
- 'propagate': True,
|
|
|
- 'level': 'DEBUG',
|
|
|
- },
|
|
|
- }
|
|
|
-}
|
|
|
-```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-[日志配置官方示例](https://docs.djangoproject.com/zh-hans/2.0/topics/logging/#s-examples)。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-#### 日志分析
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-1. Linux相关命令:head、tail、grep、awk、uniq、sort
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Shell
|
|
|
- tail -10000 access.log | awk '{print $1}' | uniq -c | sort -r
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-2. 实时日志文件分析:Python + 正则表达式 + Crontab
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-3. [《Python日志分析工具》](https://github.com/jkklee/web_log_analyse)。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-4. [《集中式日志系统ELK》](https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/opensource/os-cn-elk/index.html)。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - ElasticSearch:搜索引擎,实现全文检索。
|
|
|
- - Logstash:负责从指定节点收集日志。
|
|
|
- - Kibana:日志可视化工具。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-### RESTful
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-问题1:RESTful架构到底解决了什么问题?(URL具有自描述性、资源表述与视图的解耦和、互操作性利用构建微服务以及集成第三方系统、无状态性提高水平扩展能力)
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-问题2:项目在使用RESTful架构时有没有遇到一些问题或隐患?(对资源访问的限制、资源从属关系检查、避免泄露业务信息、防范可能的攻击)
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-> 补充:下面的几个和安全性相关的响应头在前面讲中间件的时候提到过的。
|
|
|
->
|
|
|
-> - X-Frame-Options: DENY
|
|
|
-> - X-Content-Type-Options: nosniff
|
|
|
-> - X-XSS-Protection: 1; mode=block;
|
|
|
-> - Strict-Transport-Security: max-age=31536000;
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-问题3:如何保护API中的敏感信息以及防范重放攻击?(摘要和令牌)
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-推荐阅读:[《如何有效防止API的重放攻击》](https://help.aliyun.com/knowledge_detail/50041.html)。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-#### 使用djangorestframework
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-安装djangorestfrmework(为了描述方便,以下统一简称为drf)。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-```Shell
|
|
|
-pip install djangorestframework
|
|
|
-```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-配置drf。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-```Python
|
|
|
-INSTALLED_APPS = [
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- 'rest_framework',
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-]
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-REST_FRAMEWORK = {
|
|
|
- # 配置默认页面大小
|
|
|
- 'PAGE_SIZE': 5,
|
|
|
- # 配置默认的分页类
|
|
|
- 'DEFAULT_PAGINATION_CLASS': 'rest_framework.pagination.PageNumberPagination',
|
|
|
-}
|
|
|
-```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-#### 编写序列化器
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-```Python
|
|
|
-from rest_framework import serializers
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-class HouseTypeSerializer(serializers.ModelSerializer):
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- class Meta:
|
|
|
- model = HouseType
|
|
|
- fields = '__all__'
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-class DistrictSerializer(serializers.ModelSerializer):
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- class Meta:
|
|
|
- model = District
|
|
|
- fields = ('distid', 'name', 'intro')
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-class AgentSerializer(serializers.ModelSerializer):
|
|
|
- # 如果属性需要通过代码来获取就定义为SerializerMethodField
|
|
|
- # 获取estates属性的方法应该命名为get_estates
|
|
|
- estates = serializers.SerializerMethodField()
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- @staticmethod
|
|
|
- def get_estates(agent):
|
|
|
- ret_value = []
|
|
|
- # 对于多对一外键关联(ForeignKey)可以用select_related提前加载关联属性
|
|
|
- # 通过这种方式可以使用内连接或左外连接直接获取关联属性避免1+N查询问题
|
|
|
- items = agent.estates.all().select_related('district')
|
|
|
- for item in items:
|
|
|
- ret_value.append({"estateid": item.estateid,
|
|
|
- "name": item.name,
|
|
|
- "district": DistrictSerializer(item.district).data})
|
|
|
- return ret_value
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- class Meta:
|
|
|
- model = Agent
|
|
|
- fields = ('agentid', 'name', 'tel', 'certificated', 'estates')
|
|
|
-```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-#### 方法1:使用装饰器
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-```Python
|
|
|
-@api_view(['GET'])
|
|
|
-@cache_page(timeout=None)
|
|
|
-def provinces(request):
|
|
|
- query_set = District.objects.filter(parent__isnull=True)
|
|
|
- serializer = DistrictSerializer(query_set, many=True)
|
|
|
- return JsonResponse(serializer.data, safe=False)
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-@api_view(['GET'])
|
|
|
-@cache_page(timeout=120)
|
|
|
-def districts(request, pid):
|
|
|
- query_set = District.objects.filter(parent__distid=pid)
|
|
|
- serializer = DistrictSerializer(query_set, many=True)
|
|
|
- return JsonResponse(serializer.data, safe=False)
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-```Python
|
|
|
-urlpatterns = [
|
|
|
- path('districts/', views.provinces, name='districts'),
|
|
|
- path('districts/<int:pid>', views.districts, name='district'),
|
|
|
-]
|
|
|
-```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-> 说明:上面使用了Django自带的视图装饰器(@cache_page)来实现对API接口返回数据的缓存。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-#### 方法2:使用APIView及其子类
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-更好的复用代码,不要重“复发明轮子”。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-```Python
|
|
|
-from rest_framework.generics import ListAPIView
|
|
|
-from rest_framework.response import Response
|
|
|
-from rest_framework_extensions.cache.decorators import cache_response
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-def customize_cache_key(view_instance, view_method, request, args, kwargs):
|
|
|
- """自定义缓存的key的函数"""
|
|
|
- full_path = request.get_full_path()
|
|
|
- return f'fangall:api:{full_path}'
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-class AgentDetailView(ListAPIView):
|
|
|
- queryset = Agent.objects.all()
|
|
|
- serializer_class = AgentDetailSerializer
|
|
|
- pagination_class = None
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- @cache_response(key_func=customize_cache_key)
|
|
|
- def get(self, request, agentid, *args, **kwargs):
|
|
|
- query_set = Agent.objects.filter(agentid=agentid)\
|
|
|
- .prefetch_related("estates").last()
|
|
|
- serializer = AgentDetailSerializer(query_set)
|
|
|
- return Response(serializer.data)
|
|
|
-```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-```Python
|
|
|
-urlpatterns = [
|
|
|
- path('agents/<int:agentid>', views.AgentDetailView.as_view(), name='agent'),
|
|
|
-]
|
|
|
-```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-> 说明:上面使用了drf_extensions提供的@cache_response实现了对接口数据的缓存,并使用自定义的函数来生成缓存中的key。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-#### 方法3:使用ViewSet及其子类
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-```Python
|
|
|
-class HouseTypeViewSet(CacheResponseMixin, viewsets.ModelViewSet):
|
|
|
- queryset = HouseType.objects.all()
|
|
|
- serializer_class = HouseTypeSerializer
|
|
|
- pagination_class = None
|
|
|
-```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-```Python
|
|
|
-router = DefaultRouter()
|
|
|
-router.register('housetypes', views.HouseTypeViewSet)
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-urlpatterns += router.urls
|
|
|
-```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-> 说明:上面使用了drf_extensions提供的CacheResponseMixin混入类实现了对接口数据的缓存。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-drf提供了基于Bootstrap定制的页面来显示接口返回的JSON数据,当然也可以使用[POSTMAN](https://www.getpostman.com/)这样的工具对API接口进行测试。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-#### 补充说明
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-在这里顺便提一下跟前端相关的几个问题。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-问题1:如何让浏览器能够发起DELETE/PUT/PATCH?
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-```HTML
|
|
|
-<form method="post">
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- <input type="hidden" name="_method" value="delete">
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-</form>
|
|
|
-```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-```Python
|
|
|
-if request.method == 'POST' and '_method' in request.POST:
|
|
|
- request.method = request.POST['_method'].upper()
|
|
|
-```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-```HTML
|
|
|
-<script>
|
|
|
- $.ajax({
|
|
|
- 'url': '/api/provinces',
|
|
|
- 'type': 'put',
|
|
|
- 'data': {},
|
|
|
- 'dataType': 'json',
|
|
|
- 'success': function(json) {
|
|
|
- // Web = 标签(内容) + CSS(显示) + JS(行为)
|
|
|
- // JavaScript = ES + BOM + DOM
|
|
|
- // DOM操作实现页面的局部刷新
|
|
|
- },
|
|
|
- 'error': function() {}
|
|
|
- });
|
|
|
- $.getJSON('/api/provinces', function(json) {
|
|
|
- // DOM操作实现页面的局部刷新
|
|
|
- });
|
|
|
-</script>
|
|
|
-```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-问题2:如何解决多个JavaScript库之间某个定义(如$函数)冲突的问题?
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-```HTML
|
|
|
-<script src="js/jquery.min.js"></script>
|
|
|
-<script src="js/abc.min.js"></script>
|
|
|
-<script>
|
|
|
- // $已经被后加载的JavaScript库占用了
|
|
|
- // 但是可以直接用绑定在window对象上的jQuery去代替$
|
|
|
- jQuery(function() {
|
|
|
- jQuery('#okBtn').on('click', function() {});
|
|
|
- });
|
|
|
-</script>
|
|
|
-```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-```HTML
|
|
|
-<script src="js/abc.min.js"></script>
|
|
|
-<script src="js/jquery.min.js"></script>
|
|
|
-<script>
|
|
|
- // 将$让出给其他的JavaScript库使用
|
|
|
- jQuery.noConflict();
|
|
|
- jQuery(function() {
|
|
|
- jQuery('#okBtn').on('click', function() {});
|
|
|
- });
|
|
|
-</script>
|
|
|
-```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-问题3:jQuery对象与原生DOM对象之间如何转换?
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-```HTML
|
|
|
-<button id="okBtn">点我</button>
|
|
|
-<script src="js/jquery.min.js"></script>
|
|
|
-<script>
|
|
|
- var btn = document.getElementById('okBtn'); // 原生JavaScript对象
|
|
|
- // $(btn) --> jQuery --> 拥有更多的属性和方法而且没有浏览器兼容性问题
|
|
|
- var $btn = $('#okBtn'); // jQuery对象
|
|
|
- // $btn[0] / $btn.get(0) --> JavaScript --> 自己处理浏览器兼容性问题
|
|
|
- $btn.on('click', function() {});
|
|
|
-</script>
|
|
|
-```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-#### 身份认证
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-查看drf中APIView类的代码可以看出,drf默认的认证方案是 `DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES`,如果修改authentication_classes就可以自行定制身份认证的方案。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-```Python
|
|
|
-class APIView(View):
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- # The following policies may be set at either globally, or per-view.
|
|
|
- renderer_classes = api_settings.DEFAULT_RENDERER_CLASSES
|
|
|
- parser_classes = api_settings.DEFAULT_PARSER_CLASSES
|
|
|
- authentication_classes = api_settings.DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES
|
|
|
- throttle_classes = api_settings.DEFAULT_THROTTLE_CLASSES
|
|
|
- permission_classes = api_settings.DEFAULT_PERMISSION_CLASSES
|
|
|
- content_negotiation_class = api_settings.DEFAULT_CONTENT_NEGOTIATION_CLASS
|
|
|
- metadata_class = api_settings.DEFAULT_METADATA_CLASS
|
|
|
- versioning_class = api_settings.DEFAULT_VERSIONING_CLASS
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- # 此处省略下面的代码
|
|
|
-```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-```Python
|
|
|
-DEFAULTS = {
|
|
|
- # Base API policies
|
|
|
- 'DEFAULT_RENDERER_CLASSES': (
|
|
|
- 'rest_framework.renderers.JSONRenderer',
|
|
|
- 'rest_framework.renderers.BrowsableAPIRenderer',
|
|
|
- ),
|
|
|
- 'DEFAULT_PARSER_CLASSES': (
|
|
|
- 'rest_framework.parsers.JSONParser',
|
|
|
- 'rest_framework.parsers.FormParser',
|
|
|
- 'rest_framework.parsers.MultiPartParser'
|
|
|
- ),
|
|
|
- 'DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES': (
|
|
|
- 'rest_framework.authentication.SessionAuthentication',
|
|
|
- 'rest_framework.authentication.BasicAuthentication'
|
|
|
- ),
|
|
|
- 'DEFAULT_PERMISSION_CLASSES': (
|
|
|
- 'rest_framework.permissions.AllowAny',
|
|
|
- ),
|
|
|
- 'DEFAULT_THROTTLE_CLASSES': (),
|
|
|
- 'DEFAULT_CONTENT_NEGOTIATION_CLASS': 'rest_framework.negotiation.DefaultContentNegotiation',
|
|
|
- 'DEFAULT_METADATA_CLASS': 'rest_framework.metadata.SimpleMetadata',
|
|
|
- 'DEFAULT_VERSIONING_CLASS': None,
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- # 此处省略下面的代码
|
|
|
-}
|
|
|
-```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-自定义认证类,继承`BaseAuthentication`并重写`authenticate(self, request)`方法,通过请求中的userid和token来确定用户身份。如果认证成功,该方法应返回一个二元组(用户和令牌的信息),否则产生异常。也可以重写 `authenticate_header(self, request)`方法来返回一个字符串,该字符串将用于`HTTP 401 Unauthorized`响应中的WWW-Authenticate响应头的值。如果未重写该方法,那么当未经身份验证的请求被拒绝访问时,身份验证方案将返回`HTTP 403 Forbidden`响应。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-```Python
|
|
|
-class Authentication(BaseAuthentication):
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- def authenticate(self, request):
|
|
|
- try:
|
|
|
- userid = request.GET['userid']
|
|
|
- token = request.GET['token']
|
|
|
- user = User.objects.filter(userid=userid, token=token).first()
|
|
|
- if not user:
|
|
|
- raise AuthenticationFailed('用户身份信息认证失败')
|
|
|
- return user, user
|
|
|
- except KeyError:
|
|
|
- raise NotAuthenticated('请提供当前用户身份认证信息')
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- def authenticate_header(self, request):
|
|
|
- pass
|
|
|
-```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-使用自定义的认证类。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-```Python
|
|
|
-class AgentDetailView(ListAPIView):
|
|
|
- queryset = Agent.objects.all()
|
|
|
- serializer_class = AgentDetailSerializer
|
|
|
- authentication_classes = [Authentication, ]
|
|
|
- pagination_class = None
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- @cache_response(key_func=customize_cache_key)
|
|
|
- def get(self, request, agentid, *args, **kwargs):
|
|
|
- query_set = Agent.objects.filter(agentid=agentid)\
|
|
|
- .prefetch_related("estates").last()
|
|
|
- serializer = AgentDetailSerializer(query_set)
|
|
|
- return Response(serializer.data)
|
|
|
-```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-#### 授予权限
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-权限检查总是在视图的最开始处运行,在任何其他代码被允许进行之前。最简单的权限是允许通过身份验证的用户访问,并拒绝未经身份验证的用户访问,这对应于dfr中的`IsAuthenticated`类,可以用它来取代默认的`AllowAny`类。权限策略可以在Django的drf配置中用`DEFAULT_PERMISSION_CLASSES`全局设置。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-```Python
|
|
|
-REST_FRAMEWORK = {
|
|
|
- 'DEFAULT_PERMISSION_CLASSES': (
|
|
|
- 'rest_framework.permissions.IsAuthenticated',
|
|
|
- )
|
|
|
-}
|
|
|
-```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-也可以在基于`APIView`类的视图上设置身份验证策略。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-```Python
|
|
|
-from rest_framework.permissions import IsAuthenticated
|
|
|
-from rest_framework.views import APIView
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-class ExampleView(APIView):
|
|
|
- permission_classes = (IsAuthenticated, )
|
|
|
- # 此处省略其他代码
|
|
|
-```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-或者在基于`@api_view`装饰器的视图函数上设置。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-```Python
|
|
|
-from rest_framework.decorators import api_view, permission_classes
|
|
|
-from rest_framework.permissions import IsAuthenticated
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-@api_view(['GET'])
|
|
|
-@permission_classes((IsAuthenticated, ))
|
|
|
-def example_view(request, format=None):
|
|
|
- # 此处省略其他代码
|
|
|
-```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-自定义权限需要继承`BasePermission`并实现以下方法中的一个或两个,下面是BasePermission的代码。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-```Python
|
|
|
-@six.add_metaclass(BasePermissionMetaclass)
|
|
|
-class BasePermission(object):
|
|
|
- """
|
|
|
- A base class from which all permission classes should inherit.
|
|
|
- """
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- def has_permission(self, request, view):
|
|
|
- """
|
|
|
- Return `True` if permission is granted, `False` otherwise.
|
|
|
- """
|
|
|
- return True
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- def has_object_permission(self, request, view, obj):
|
|
|
- """
|
|
|
- Return `True` if permission is granted, `False` otherwise.
|
|
|
- """
|
|
|
- return True
|
|
|
-```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-如果请求被授予访问权限,则方法应该返回True,否则返False。下面的例子演示了阻止黑名单中的IP地址访问接口数据(这个在反爬虫的时候很有用哟)。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-```Python
|
|
|
-from rest_framework import permissions
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-class BlacklistPermission(permissions.BasePermission):
|
|
|
- """
|
|
|
- Global permission check for blacklisted IPs.
|
|
|
- """
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- def has_permission(self, request, view):
|
|
|
- ip_addr = request.META['REMOTE_ADDR']
|
|
|
- blacklisted = Blacklist.objects.filter(ip_addr=ip_addr).exists()
|
|
|
- return not blacklisted
|
|
|
-```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-如果要实现更为完整的权限验证,可以考虑RBAC或ACL。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-1. RBAC - 基于角色的访问控制(用户-角色-权限-资源,都是多对多关系)。
|
|
|
-2. ACL - 访问控制列表(每个用户绑定自己的访问白名单)。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-#### 访问限流
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-可以修改dfr配置的`DEFAULT_THROTTLE_CLASSES` 和 `DEFAULT_THROTTLE_RATES`两个值来设置全局默认限流策略。例如:
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-```Python
|
|
|
-REST_FRAMEWORK = {
|
|
|
- 'DEFAULT_THROTTLE_CLASSES': (
|
|
|
- 'rest_framework.throttling.AnonRateThrottle',
|
|
|
- 'rest_framework.throttling.UserRateThrottle'
|
|
|
- ),
|
|
|
- 'DEFAULT_THROTTLE_RATES': {
|
|
|
- 'anon': '100/day',
|
|
|
- 'user': '1000/day'
|
|
|
- }
|
|
|
-}
|
|
|
-```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-`DEFAULT_THROTTLE_RATES`中使用的频率描述可能包括`second`、`minute`、`hour`或`day`。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-如果要为接口单独设置限流,可以在每个视图或视图集上设置限流策略,如下所示:
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-```Python
|
|
|
-from rest_framework.throttling import UserRateThrottle
|
|
|
-from rest_framework.views import APIView
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-class ExampleView(APIView):
|
|
|
- throttle_classes = (UserRateThrottle, )
|
|
|
- # 此处省略下面的代码
|
|
|
-```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-或
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-```Python
|
|
|
-@api_view(['GET'])
|
|
|
-@throttle_classes([UserRateThrottle, ])
|
|
|
-def example_view(request, format=None):
|
|
|
- # 此处省略下面的代码
|
|
|
-```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-当然也可以通过继承`BaseThrottle`来自定义限流策略,需要重写`allow_request`和`wait`方法。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-### 异步任务和计划任务
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-#### Celery的应用
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
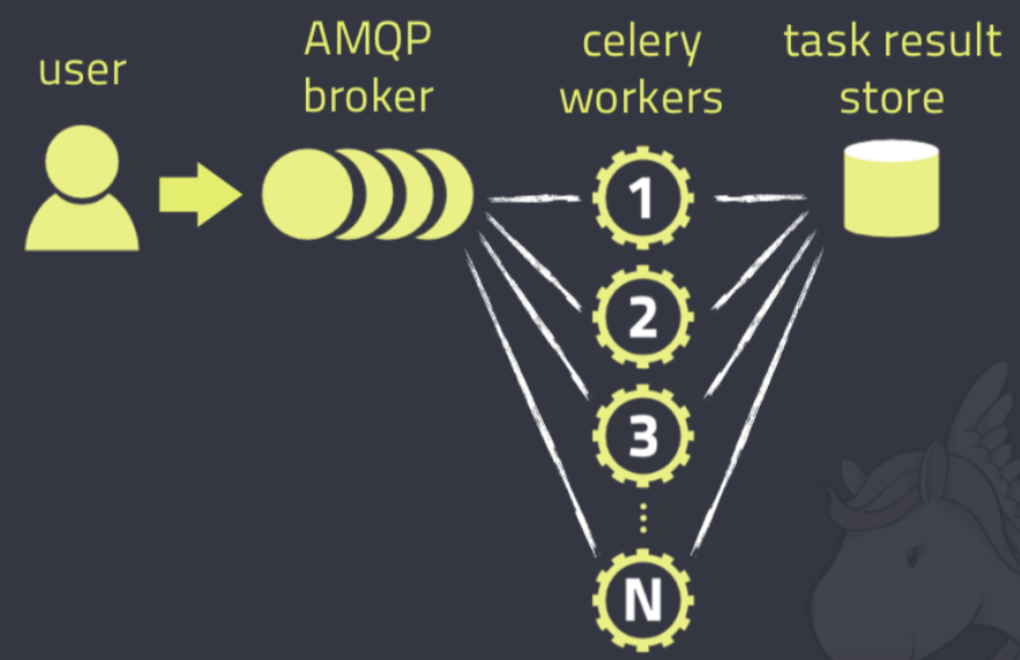
-Celery 是一个简单、灵活且可靠的,处理大量消息的分布式系统,并且提供维护这样一个系统的必需工具。它是一个专注于实时处理的任务队列,同时也支持任务调度。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-推荐阅读:[《Celery官方文档中文版》](http://docs.jinkan.org/docs/celery/),上面有极为详细的配置和使用指南。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-Celery是一个本身不提供队列服务,官方推荐使用RabbitMQ或Redis来实现消息队列服务,前者是更好的选择,它对AMQP(高级消息队列协议)做出了非常好的实现。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-1. 安装RabbitMQ。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Shell
|
|
|
- docker pull rabbitmq
|
|
|
- docker run -d -p 5672:5672 --name myrabbit rabbitmq
|
|
|
- docker container exec -it myrabbit /bin/bash
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-2. 创建用户、资源以及分配操作权限。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Shell
|
|
|
- rabbitmqctl add_user luohao 123456
|
|
|
- rabbitmqctl set_user_tags luohao administrator
|
|
|
- rabbitmqctl add_vhost vhost1
|
|
|
- rabbitmqctl set_permissions -p vhost1 luohao ".*" ".*" ".*"
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-3. 创建Celery实例。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Python
|
|
|
- project_name = '...'
|
|
|
- project_settings = '%s.settings' % project_name
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- # 注册环境变量
|
|
|
- os.environ.setdefault('DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE', project_settings)
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- app = celery.Celery(
|
|
|
- project_name,
|
|
|
- broker='amqp://luohao:123456@120.77.222.217:5672/vhost1'
|
|
|
- )
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- # 从默认的配置文件读取配置信息
|
|
|
- app.config_from_object('django.conf:settings')
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- # Celery加载所有注册的应用
|
|
|
- app.autodiscover_tasks(lambda: settings.INSTALLED_APPS)
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-4. 启动Celery创建woker(消息的消费者)。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Shell
|
|
|
- celery -A <projname> worker -l debug &
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-5. 执行异步任务。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Python
|
|
|
- @app.task
|
|
|
- def send_email(from, to, cc, subject, content):
|
|
|
- pass
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- send_email.delay('', [], [], '', '')
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-6. 创建定时任务。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Python
|
|
|
- # 配置定时任务(计划任务)
|
|
|
- app.conf.update(
|
|
|
- timezone=settings.TIME_ZONE,
|
|
|
- enable_utc=True,
|
|
|
- # 定时任务(计划任务)相当于是消息的生产者
|
|
|
- # 如果只有生产者没有消费者那么消息就会在消息队列中积压
|
|
|
- # 将来实际部署项目的时候生产者、消费者、消息队列可能都是不同节点
|
|
|
- beat_schedule={
|
|
|
- 'task1': {
|
|
|
- 'task': 'common.tasks.show_msg',
|
|
|
- 'schedule': crontab(),
|
|
|
- 'args': ('刘强东,奶茶妹妹喊你回家喝奶啦', )
|
|
|
- },
|
|
|
- },
|
|
|
- )
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Python
|
|
|
- @app.task
|
|
|
- def show_msg(content):
|
|
|
- print(content)
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-7. 启动Celery创建执行定时任务的beat(消息的生产者)。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Shell
|
|
|
- celery -A <projname> beat -l info
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-8. 检查消息队列状况。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Shell
|
|
|
- rabbitmqctl list_queues -p vhost1
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-### 其他问题
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-问题1:如何解决JavaScript跨域获取数据的问题?(django-cors-headers)
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-```Python
|
|
|
-INSTALLED_APPS = [
|
|
|
- 'corsheaders',
|
|
|
-]
|
|
|
-MIDDLEWARE = [
|
|
|
- 'corsheaders.middleware.CorsMiddleware',
|
|
|
-]
|
|
|
-# 配置跨域白名单
|
|
|
-# CORS_ORIGIN_WHITELIST = ()
|
|
|
-# 配置是否跨域读取Cookie信息
|
|
|
-# CORS_ALLOW_CREDENTIALS = True
|
|
|
-```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-问题2:网站图片(水印、剪裁)和视频(截图、水印、转码)是如何处理的?(云存储、FFmpeg)
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-问题3:网站如何架设(静态资源)文件系统?(FastDFS、云存储、CDN)
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-### 安全保护
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-问题1:什么是跨站脚本攻击,如何防范?(对提交的内容进行消毒)
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-问题2:什么是跨站身份伪造,如何防范?(使用随机令牌)
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-问题3:什么是SQL注射攻击,如何防范?(不拼接SQL语句,避免使用单引号)
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-问题4:什么是点击劫持攻击,如何防范?(不允许`<iframe>`加载非同源站点内容)
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-#### Django提供的安全措施
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-签名数据的API
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Python
|
|
|
->>> from django.core.signing import Signer
|
|
|
->>> signer = Signer()
|
|
|
->>> value = signer.sign('hello, world!')
|
|
|
->>> value
|
|
|
-'hello, world!:BYMlgvWMTSPLxC-DqxByleiMVXU'
|
|
|
->>> signer.unsign(value)
|
|
|
-'hello, world!'
|
|
|
->>>
|
|
|
->>> signer = Signer(salt='1qaz2wsx')
|
|
|
->>> signer.sign('hello, world!')
|
|
|
-'hello, world!:9vEvG6EA05hjMDB5MtUr33nRA_M'
|
|
|
->>>
|
|
|
->>> from django.core.signing import TimestampSigner
|
|
|
->>> signer = TimestampSigner()
|
|
|
->>> value = signer.sign('hello, world!')
|
|
|
->>> value
|
|
|
-'hello, world!:1fpmcQ:STwj464IFE6eUB-_-hyUVF3d2So'
|
|
|
->>> signer.unsign(value, max_age=5)
|
|
|
-Traceback (most recent call last):
|
|
|
- File "<console>", line 1, in <module>
|
|
|
- File "/Users/Hao/Desktop/fang.com/venv/lib/python3.6/site-packages/django/core/signing.py", line 198, in unsign
|
|
|
- 'Signature age %s > %s seconds' % (age, max_age))
|
|
|
- django.core.signing.SignatureExpired: Signature age 21.020604848861694 > 5 seconds
|
|
|
->>> signer.unsign(value, max_age=120)
|
|
|
-'hello, world!'
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-CSRF令牌和小工具
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-```HTML
|
|
|
-{% csrf_token %}
|
|
|
-```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-- @csrf_exempt:免除令牌
|
|
|
-- @csrf_protect:提供令牌保护
|
|
|
-- @require_csrf_token:提供令牌保护
|
|
|
-- @ensure_csrf_cookie:强制视图发送带令牌的cookie
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-> 说明:可以在Chrome浏览器中安装EditThisCookie插件来方便的查看Cookie。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-#### 用户敏感信息的保护
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-1. 哈希摘要(签名)
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Python
|
|
|
- >>> import hashlib
|
|
|
- >>>
|
|
|
- >>> md5_hasher = hashlib.md5()
|
|
|
- >>> md5_hasher.update('hello, world!'.encode())
|
|
|
- >>> md5_hasher.hexdigest()
|
|
|
- '3adbbad1791fbae3ec908894c4963870'
|
|
|
- >>>
|
|
|
- >>> sha1_hasher = hashlib.sha1()
|
|
|
- >>> sha1_hasher.update('hello, world!'.encode())
|
|
|
- >>> sha1_hasher.update('goodbye, world!'.encode())
|
|
|
- >>> sha1_hasher.hexdigest()
|
|
|
- '1f09d30c707d53f3d16c530dd73d70a6ce7596a9'
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-2. 加密和解密(对称加密[AES]和非对称加密[RSA])
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Shell
|
|
|
- pip install rsa
|
|
|
- pip install pycrypto
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Python
|
|
|
- >>> pub_key, pri_key = rsa.newkeys(1024)
|
|
|
- >>> message = 'hello, world!'
|
|
|
- >>> crypto = rsa.encrypt(message.encode(), pub_key)
|
|
|
- >>> crypto
|
|
|
- b'Ou{gH\xa9\xa8}O\xe3\x1d\x052|M\x9d9?\xdc\xd8\xecF\xd3v\x9b\xde\x8e\x12\xe6M\xebvx\x08\x08\x8b\xe8\x86~\xe4^)w\xf2\xef\x9e\x9fOg\x15Q\xb7\x7f\x1d\xcfV\xf1\r\xbe^+\x8a\xbf }\x10\x01\xa4U9b\x97\xf5\xe0\x90T\'\xd4(\x9b\x00\xa5\x92\x17\xad4\xb0\xb0"\xd4\x16\x94*s\xe1r\xb7L\xe2\x98\xb7\x7f\x03\xd9\xf2\t\xee*\xe6\x93\xe6\xe1o\xfd\x18\x83L\x0cfL\xff\xe4\xdd%\xf2\xc0/\xfb'
|
|
|
- >>> origin = rsa.decrypt(crypto, pri_key).decode()
|
|
|
- >>> origin
|
|
|
- 'hello, world!'
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-#### 安全相关建议
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-1. 虽然 Django 自带了稳固的安全保护措施,但是依然要采用正确的方式部署应用程序,利用 Web 服务器、操作系统和其他组件提供的安全保护措施。
|
|
|
-2. 记得把 Python 代码放在 Web 服务器的文档根目录之外,避免代码意外泄露。
|
|
|
-3. 谨慎处理用户上传的文件。
|
|
|
-4. Django本身没有对请求次数加以限制(包括验证用户身份的请求),为了防止暴力攻击和破解,可以考虑使用具有一次消费性的验证码或对这类请求的次数进行限制。
|
|
|
-5. 将缓存系统、数据库服务器以及重要的资源服务器都放在第二级防火墙之后(不要放在DMZ)。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-### 测试相关
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-测试是发现和标记缺陷的过程。所谓的缺陷是指实际结果和期望结果之间的任何差别。有的地方,测试也被认为是执行以找出错误为目的的程序的过程。 测试是为了让产品达到以下目标:
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-1. 满足需求用户满意
|
|
|
-2. 改善产品的市场占有率
|
|
|
-3. 树立对产品的信任
|
|
|
-4. 减少开发和维护的成本
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-#### 功能测试
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-如果一个软件单元的行为方式与它的开发规范完全一样,那么该软件单元就通过了它的功能测试。
|
|
|
- - 白盒测试:开发人员自己实现,最基本的形式是单元测试,还有集成测试和系统测试。
|
|
|
- - 黑盒测试:由开发团队之外的人执行,对测试代码没有可见性,将被测系统视为黑盒子。通常由测试人员或QA工程师来执行,Web应用可以通过Selenium这样的测试框架自动化实施。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-#### 性能测试
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-软件在高工作负载下对其响应性和健壮性展开的测试。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-- 负载测试:在特定负载下执行的测试。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - 压力测试:突发条件或极限条件下的性能测试。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-#### 安全性测试
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-系统的敏感数据都是经过认证和授权之后才能访问。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-#### 其他测试
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-易用性测试 / 安装测试 / 可访问性测试
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-#### 单元测试
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-测试函数和对象的方法(程序中最小最基本的单元)。通过对实际输出和预期输出的比对以及各种的断言条件来判定被测单元是否满足设计需求。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-- 测试用例
|
|
|
-- 测试固件 - 每次测试时都要使用的东西。
|
|
|
-- 测试套件(测试集)- 组合了多个测试用例而构成的集合。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-```Python
|
|
|
-class UtilTest(TestCase):
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- def setUp(self):
|
|
|
- self.pattern = re.compile(r'\d{6}')
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- def test_gen_mobile_code(self):
|
|
|
- for _ in range(100):
|
|
|
- self.assertIsNotNone(self.pattern.match(gen_mobile_code()))
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- def test_to_md5_hex(self):
|
|
|
- md5_dict = {
|
|
|
- '123456': 'e10adc3949ba59abbe56e057f20f883e',
|
|
|
- '123123123': 'f5bb0c8de146c67b44babbf4e6584cc0',
|
|
|
- '1qaz2wsx': '1c63129ae9db9c60c3e8aa94d3e00495',
|
|
|
- }
|
|
|
- for key, value in md5_dict.items():
|
|
|
- self.assertEqual(value, to_md5_hex(key))
|
|
|
-```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-`TestCase`的断言方法:
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-- assertEqual / assertNotEqual
|
|
|
-- assertTrue / assertFalse / assertIsNot
|
|
|
-- assertRaise / assertRaiseRegexp
|
|
|
-- assertAlmostEqual / assertNotAlmostEqual
|
|
|
-- assertGreater / assertGreaterEqual / assertLess / assertLessEqual
|
|
|
-- assertRegexpMatches / assertNotRegexpMatches
|
|
|
-- assertListEqual / assertSetEqual / assertTupleEqual / assertDictEqual
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-可以使用nose2或pytest来辅助执行单元测试,同时通过cov-core或pytest-cov可以对测试覆度进行评估。覆盖率由百分比表示。比如测试代码执行过了程序的每一行,那么覆盖率就是100%。这种时候,几乎不会出现新程序上线后突然无法运行的尴尬情况。覆盖率不关心代码内容究竟是什么,覆盖率是用来检查“测试代码不足、测试存在疏漏”的一个指标,“测试内容是否妥当”并不归它管。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-```Shell
|
|
|
-pip install nose2 pytest cov-core pytest-cov
|
|
|
-```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-可以使用Selenium来实现Web应用的自动化测试,它还可以用于屏幕抓取与浏览器行为模拟,通过爬虫抓取页面上的动态数据也可以使用它。Selenium其实包括三个部分:
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-- Selenium IDE:嵌入到浏览器的插件,可以录制和回放脚本。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- 
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-- Selenium WebDriver:支持多种语言可以操控浏览器的API。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-- Selenium Standalone Server:Selenium Grid、远程控制、分布式部署。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-```Shell
|
|
|
-pip install selenium
|
|
|
-```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-```Python
|
|
|
-from selenium import webdriver
|
|
|
-import pytest
|
|
|
-import contextlib
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-@pytest.fixture(scope='session')
|
|
|
-def chrome():
|
|
|
- # 设置使用无头浏览器(不会打开浏览器窗口)
|
|
|
- options = webdriver.ChromeOptions()
|
|
|
- options.add_argument('--headless')
|
|
|
- driver = webdriver.Chrome(options=options)
|
|
|
- yield driver
|
|
|
- driver.quit()
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-def test_baidu_index(chrome):
|
|
|
- chrome.get('https://www.baidu.com')
|
|
|
- assert chrome.title == '百度一下,你就知道'
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-```Shell
|
|
|
-nose2 -v -C
|
|
|
-pytest --cov
|
|
|
-```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-```Shell
|
|
|
-Ran 7 tests in 0.002s
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-OK
|
|
|
-Name Stmts Miss Cover
|
|
|
-----------------------------------------------
|
|
|
-example01.py 15 0 100%
|
|
|
-example02.py 49 49 0%
|
|
|
-example03.py 22 22 0%
|
|
|
-example04.py 61 61 0%
|
|
|
-example05.py 29 29 0%
|
|
|
-example06.py 39 39 0%
|
|
|
-example07.py 19 19 0%
|
|
|
-example08.py 27 27 0%
|
|
|
-example09.py 18 18 0%
|
|
|
-example10.py 19 19 0%
|
|
|
-example11.py 22 22 0%
|
|
|
-example12.py 28 28 0%
|
|
|
-example13.py 28 28 0%
|
|
|
-test_ddt_example.py 18 0 100%
|
|
|
-test_pytest_example.py 11 6 45%
|
|
|
-test_unittest_example.py 22 0 100%
|
|
|
-----------------------------------------------
|
|
|
-TOTAL 427 367 14%
|
|
|
-```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-在测试过程中需要孤立各种外部依赖(数据库、外部接口调用、时间依赖),具体又包括两个方面:
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-1. 数据源:数据本地化 / 置于内存中 / 测试之后回滚
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-2. 资源虚拟化:存根/桩(stub)、仿制/模拟(mock)、伪造(fake)
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - stub:测试期间为提供响应的函数生成的替代品
|
|
|
- - mock:代替实际对象(以及该对象的API)的对象
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - fake:没有达到生产级别的轻量级对象
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-#### 集成测试
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-集成多个函数或方法的输入输出的测试,测试时需要将多个测试对象组合在一起。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - 测试组件互操作性 / 需求变更测试 / 外部依赖和API / 调试硬件问题 / 在代码路径中发现异常
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-#### 系统测试
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-对需求的测试,测试成品是否最终满足了所有需求,在客户验收项目时进行。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-#### 数据驱动测试
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-使用外部数据源实现对输入值与期望值的参数化,避免在测试中使用硬编码的数据。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-被测函数:
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-```Python
|
|
|
-def add(x, y):
|
|
|
- return x + y
|
|
|
-```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-data.csv文件:
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-```
|
|
|
-3,1,2
|
|
|
-0,1,-1
|
|
|
-100,50,50
|
|
|
-100,1,99
|
|
|
-15,7,8
|
|
|
-```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-测试代码:
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-```Python
|
|
|
-import csv
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-from unittest import TestCase
|
|
|
-from ddt import ddt, data, unpack
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-@ddt
|
|
|
-class TestAdd(TestCase):
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- def load_data_from_csv(filename):
|
|
|
- data_items = []
|
|
|
- with open(filename, 'r', newline='') as fs:
|
|
|
- reader = csv.reader(fs)
|
|
|
- for row in reader:
|
|
|
- data_items.append(list(map(int, row)))
|
|
|
- return data_items
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- @data(*load_data_from_csv('data.csv'))
|
|
|
- @unpack
|
|
|
- def test_add(self, result, param1, param2):
|
|
|
- self.assertEqual(result, add(param1, param2))
|
|
|
-```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-#### Django中的测试
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-1. 测试Django视图 - Django中提供的`TestCase`扩展了`unittest`中的`TestCase`,绑定了一个名为`client`的属性,可以用来模拟浏览器发出的GET、POST、DELETE、PUT等请求。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-```Python
|
|
|
-class SomeViewTest(TestCase):
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- def test_example_view(self):
|
|
|
- resp = self.client.get(reverse('index'))
|
|
|
- self.assertEqual(200, resp.status_code)
|
|
|
- self.assertEqual(5, resp.context['num'])
|
|
|
-```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-2. 运行测试 - 配置测试数据库。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-```Python
|
|
|
-DATABASES = {
|
|
|
- 'default': {
|
|
|
- 'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.mysql',
|
|
|
- 'HOST': 'localhost',
|
|
|
- 'PORT': 3306,
|
|
|
- 'NAME': 'DbName',
|
|
|
- 'USER': os.environ['DB_USER'],
|
|
|
- 'PASSWORD': os.environ['DB_PASS'],
|
|
|
- 'TEST': {
|
|
|
- 'NAME': 'DbName_for_testing',
|
|
|
- 'CHARSET': 'utf8',
|
|
|
- },
|
|
|
- }
|
|
|
-}
|
|
|
-```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-```Shell
|
|
|
-python manage.py test
|
|
|
-python manage.py test common
|
|
|
-python manage.py test common.tests.UtilsTest
|
|
|
-python manage.py test common.tests.UtilsTest.test_to_md5_hex
|
|
|
-```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-3. 评估测试覆盖度
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-```Shell
|
|
|
-pip install coverage
|
|
|
-coverage run --source=<path1> --omit=<path2> manage.py test common
|
|
|
-coverage report
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-Name Stmts Miss Cover
|
|
|
----------------------------------------------------
|
|
|
-common/__init__.py 0 0 100%
|
|
|
-common/admin.py 1 0 100%
|
|
|
-common/apps.py 3 3 0%
|
|
|
-common/forms.py 16 16 0%
|
|
|
-common/helper.py 32 32 0%
|
|
|
-common/middlewares.py 19 19 0%
|
|
|
-common/migrations/__init__.py 0 0 100%
|
|
|
-common/models.py 71 2 97%
|
|
|
-common/serializers.py 14 14 0%
|
|
|
-common/tests.py 14 8 43%
|
|
|
-common/urls_api.py 3 3 0%
|
|
|
-common/urls_user.py 3 3 0%
|
|
|
-common/utils.py 22 7 68%
|
|
|
-common/views.py 69 69 0%
|
|
|
----------------------------------------------------
|
|
|
-TOTAL 267 176 34%
|
|
|
-```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-#### 性能测试
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-问题1:性能测试的指标有哪些?
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-1. ab - Apache Benchmark / webbench / httpperf
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Shell
|
|
|
- yum -y install httpd
|
|
|
- ab -c 10 -n 1000 http://www.baidu.com/
|
|
|
- ...
|
|
|
- Benchmarking www.baidu.com (be patient).....done
|
|
|
- Server Software: BWS/1.1
|
|
|
- Server Hostname: www.baidu.com
|
|
|
- Server Port: 80
|
|
|
- Document Path: /
|
|
|
- Document Length: 118005 bytes
|
|
|
- Concurrency Level: 10
|
|
|
- Time taken for tests: 0.397 seconds
|
|
|
- Complete requests: 100
|
|
|
- Failed requests: 98
|
|
|
- (Connect: 0, Receive: 0, Length: 98, Exceptions: 0)
|
|
|
- Write errors: 0
|
|
|
- Total transferred: 11918306 bytes
|
|
|
- HTML transferred: 11823480 bytes
|
|
|
- Requests per second: 252.05 [#/sec] (mean)
|
|
|
- Time per request: 39.675 [ms] (mean)
|
|
|
- Time per request: 3.967 [ms] (mean, across all concurrent requests)
|
|
|
- Transfer rate: 29335.93 [Kbytes/sec] received
|
|
|
- Connection Times (ms)
|
|
|
- min mean[+/-sd] median max
|
|
|
- Connect: 6 7 0.6 7 9
|
|
|
- Processing: 20 27 22.7 24 250
|
|
|
- Waiting: 8 11 21.7 9 226
|
|
|
- Total: 26 34 22.8 32 258
|
|
|
- Percentage of the requests served within a certain time (ms)
|
|
|
- 50% 32
|
|
|
- 66% 34
|
|
|
- 75% 34
|
|
|
- 80% 34
|
|
|
- 90% 36
|
|
|
- 95% 39
|
|
|
- 98% 51
|
|
|
- 99% 258
|
|
|
- 100% 258 (longest request)
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-2. mysqlslap
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Shell
|
|
|
- mysqlslap -a -c 100 -h 1.2.3.4 -u root -p
|
|
|
- mysqlslap -a -c 100 --number-of-queries=1000 --auto-generate-sql-load-type=read -h <负载均衡服务器IP地址> -u root -p
|
|
|
- mysqlslap -a --concurrency=50,100 --number-of-queries=1000 --debug-info --auto-generate-sql-load-type=mixed -h 1.2.3.4 -u root -p
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-3. sysbench
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Shell
|
|
|
- sysbench --test=threads --num-threads=64 --thread-yields=100 --thread-locks=2 run
|
|
|
- sysbench --test=memory --num-threads=512 --memory-block-size=256M --memory-total-size=32G run
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-4. jmeter
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- 请查看[《使用JMeter进行性能测试》](https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/java/l-jmeter/index.html)。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-5. LoadRunner / QTP
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-### 项目调试
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-可以使用django-debug-toolbar来辅助项目调试。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-1. 安装
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Shell
|
|
|
- pip install django-debug-toolbar
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-2. 配置 - 修改settings.py。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Python
|
|
|
- INSTALLED_APPS = [
|
|
|
- 'debug_toolbar',
|
|
|
- ]
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- MIDDLEWARE = [
|
|
|
- 'debug_toolbar.middleware.DebugToolbarMiddleware',
|
|
|
- ]
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- DEBUG_TOOLBAR_CONFIG = {
|
|
|
- # 引入jQuery库
|
|
|
- 'JQUERY_URL': 'https://cdn.bootcss.com/jquery/3.3.1/jquery.min.js',
|
|
|
- # 工具栏是否折叠
|
|
|
- 'SHOW_COLLAPSED': True,
|
|
|
- # 是否显示工具栏
|
|
|
- 'SHOW_TOOLBAR_CALLBACK': lambda x: True,
|
|
|
- }
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-3. 配置 - 修改urls.py。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Python
|
|
|
- if settings.DEBUG:
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- import debug_toolbar
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- urlpatterns.insert(0, path('__debug__/', include(debug_toolbar.urls)))
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-4. 使用 - 在页面右侧可以看到一个调试工具栏,上面包括了执行时间、项目设置、请求头、SQL、静态资源、模板、缓存、信号等调试信息,查看起来非常的方便。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-### 部署相关
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-请参考《Django项目上线指南》。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-### 性能相关
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-#### 网站优化两大定律:
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-1. 尽可能的使用缓存 - 牺牲空间换取时间(普适策略)。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-2. 能推迟的都推迟 - 使用消息队列将并行任务串行来缓解服务器压力。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - 服务器CPU利用率出现瞬时峰值 - 削峰(CPU利用率平缓的增长)
|
|
|
- - 上下游节点解耦合(下订单和受理订单的系统通常是分离的)
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-#### Django框架
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-1. 配置缓存来缓解数据库的压力,并有合理的机制应对[缓存穿透和缓存雪崩](https://www.cnblogs.com/zhangweizhong/p/6258797.html)。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-2. 开启[模板缓存](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/2.0/ref/templates/api/#django.template.loaders.cached.Loader)来加速模板的渲染。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Python
|
|
|
- TEMPLATES = [
|
|
|
- {
|
|
|
- 'BACKEND': 'django.template.backends.django.DjangoTemplates',
|
|
|
- 'DIRS': [os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'templates'), ],
|
|
|
- # 'APP_DIRS': True,
|
|
|
- 'OPTIONS': {
|
|
|
- 'context_processors': [
|
|
|
- 'django.template.context_processors.debug',
|
|
|
- 'django.template.context_processors.request',
|
|
|
- 'django.contrib.auth.context_processors.auth',
|
|
|
- 'django.contrib.messages.context_processors.messages',
|
|
|
- ],
|
|
|
- 'loaders': [(
|
|
|
- 'django.template.loaders.cached.Loader', [
|
|
|
- 'django.template.loaders.filesystem.Loader',
|
|
|
- 'django.template.loaders.app_directories.Loader',
|
|
|
- ], ),
|
|
|
- ],
|
|
|
- },
|
|
|
- },
|
|
|
- ]
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-3. 用惰性求值、迭代器、`defer()`、`only()`等缓解内存压力。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-4. 用`select_related()`和`prefetch_related()`执行预加载避免“1+N查询问题”。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-#### 数据库
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-1. 用ID生成器代替自增主键(性能更好、适用于分布式环境)。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - 自定义ID生成器
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - UUID
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Python
|
|
|
- >>> my_uuid = uuid.uuid1()
|
|
|
- >>> my_uuid
|
|
|
- UUID('63f859d0-a03a-11e8-b0ad-60f81da8d840')
|
|
|
- >>> my_uuid.hex
|
|
|
- '63f859d0a03a11e8b0ad60f81da8d840'
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-2. 避免不必要的外键列上的约束(除非必须保证参照完整性),更不要使用触发器之类的机制。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-3. 使用索引来优化查询性能(索引放在要用于查询的字段上)。InnoDB用的是BTREE索引,使用>、<、>=、<=、BETWEEN或者LIKE 'pattern'(pattern不以通配符开头)时都可以用到索引。因为建立索引需要额外的磁盘空间,而主键上是有默认的索引,所以主键要尽可能选择较短的数据类型来减少磁盘占用,提高索引的缓存效果。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```SQL
|
|
|
- create index idx_goods_name on tb_goods (gname(10));
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```SQL
|
|
|
- -- 无法使用索引
|
|
|
- select * from tb_goods where gname like '%iPhone%';
|
|
|
- -- 可以使用索引
|
|
|
- select * from tb_goods where gname like 'iPhone%';
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Python
|
|
|
- # 无法使用索引
|
|
|
- Goods.objects.filter(name_icontains='iPhone')
|
|
|
- # 可以使用索引
|
|
|
- Goods.objects.filter(name__istartswith='iPhone');
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-4. 使用存储过程(存储在服务器端编译过的一组SQL语句)。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```SQL
|
|
|
- drop procedure if exists sp_avg_sal_by_dept;
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- create procedure sp_avg_sal_by_dept(deptno integer, out avg_sal float)
|
|
|
- begin
|
|
|
- select avg(sal) into avg_sal from TbEmp where dno=deptno;
|
|
|
- end;
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- call sp_avg_sal_by_dept(10, @a);
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- select @a;
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```Python
|
|
|
- >>> from django.db import connection
|
|
|
- >>> cursor = connection.cursor()
|
|
|
- >>> cursor.callproc('sp_avg_sal_by_dept', (10, 0))
|
|
|
- >>> cursor.execute('select @_sp_avg_sal_by_dept_1')
|
|
|
- >>> cursor.fetchone()
|
|
|
- (2675.0,)
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-5. 使用数据分区。通过分区可以存储更多的数据、优化查询更大的吞吐量、可以快速删除过期的数据。关于这个知识点可以看看MySQL的[官方文档](https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/partitioning-overview.html)。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - RANGE分区:基于连续区间范围,把数据分配到不同的分区。
|
|
|
- - LIST分区:基于枚举值的范围,把数据分配到不同的分区。
|
|
|
- - HASH分区 / KEY分区:基于分区个数,把数据分配到不同的分区。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```SQL
|
|
|
- CREATE TABLE tb_emp (
|
|
|
- eno INT NOT NULL,
|
|
|
- ename VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL,
|
|
|
- job VARCHAR(10) NOT NULL,
|
|
|
- hiredate DATE NOT NULL,
|
|
|
- dno INT NOT NULL
|
|
|
- )
|
|
|
- PARTITION BY HASH(dno)
|
|
|
- PARTITIONS 4;
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```SQL
|
|
|
- CREATE TABLE tb_emp (
|
|
|
- eno INT NOT NULL,
|
|
|
- ename VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL,
|
|
|
- job VARCHAR(10) NOT NULL,
|
|
|
- hiredate DATE NOT NULL,
|
|
|
- dno INT NOT NULL
|
|
|
- )
|
|
|
- PARTITION BY RANGE( YEAR(hiredate) ) (
|
|
|
- PARTITION p0 VALUES LESS THAN (1960),
|
|
|
- PARTITION p1 VALUES LESS THAN (1970),
|
|
|
- PARTITION p2 VALUES LESS THAN (1980),
|
|
|
- PARTITION p3 VALUES LESS THAN (1990),
|
|
|
- PARTITION p4 VALUES LESS THAN MAXVALUE
|
|
|
- );
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-6. 使用`explain`来分析查询性能 - 执行计划。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```SQL
|
|
|
- explain select * from ...;
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- `explain`结果解析:
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- - select_type:表示select操作的类型,常见的值有SIMPLE(简单查询,没有使用子查询或者表连接查询)、PRIMARY(主查询,外层的查询)、UNION(并集操作中的第二个或者后面的查询)、SUBQUERY(子查询中的第一个SELECT)等。
|
|
|
- - table:输出结果的表。
|
|
|
- - type:MySQL在表中找到所需行的方式,也称为访问类型,常见的值有:
|
|
|
- - ALL:全表扫描(遍历全表找到匹配的行)
|
|
|
- - index:索引全扫描(遍历整个索引)
|
|
|
- - range:索引范围扫描
|
|
|
- - ref:非唯一索引扫描或唯一索引的前缀扫描
|
|
|
- - eq_ref:唯一索引扫描
|
|
|
- - const / system:表中最多有一行匹配
|
|
|
- - NULL:不用访问表或者索引
|
|
|
- - possible_keys:查询时可能用到的索引。
|
|
|
- - key:实际使用的索引。
|
|
|
- - key_len:使用到索引字段的长度。
|
|
|
- - rows:扫描行的数量。
|
|
|
- - Extra:额外的信息(执行情况的说明或描述)。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- > 说明:关于MySQL更多的知识尤其是性能调优和运维方面的内容,推荐大家阅读网易出品的《深入浅出MySQL(第2版)》,网易出品必属精品。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-7. 使用慢查询日志来发现性能低下的查询。
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```SQL
|
|
|
- mysql> show variables like 'slow_query%';
|
|
|
- +---------------------------+----------------------------------+
|
|
|
- | Variable_name | Value |
|
|
|
- +---------------------------+----------------------------------+
|
|
|
- | slow_query_log | OFF |
|
|
|
- | slow_query_log_file | /mysql/data/localhost-slow.log |
|
|
|
- +---------------------------+----------------------------------+
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- mysql> show variables like 'long_query_time';
|
|
|
- +-----------------+-----------+
|
|
|
- | Variable_name | Value |
|
|
|
- +-----------------+-----------+
|
|
|
- | long_query_time | 10.000000 |
|
|
|
- +-----------------+-----------+
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```SQL
|
|
|
- mysql> set global slow_query_log='ON';
|
|
|
- mysql> set global long_query_time=1;
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- ```INI
|
|
|
- [mysqld]
|
|
|
- slow_query_log = ON
|
|
|
- slow_query_log_file = /usr/local/mysql/data/slow.log
|
|
|
- long_query_time = 1
|
|
|
- ```
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-#### 其他
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-请参考《Python性能调优》。
|